init
This commit is contained in:
commit
50392947b6
1
.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
1
.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
*.dio
|
||||
69
01. Promise基础/1.js
Normal file
69
01. Promise基础/1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
// onFulffiled: 成功后的回调
|
||||
// onRejected: 失败后的回调
|
||||
function sendMessage(name, onFulffiled, onRejected) {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
onFulffiled(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
onRejected(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 首先向 李建国 发送消息
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'李建国',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,输出回复的消息后,向 王富贵 发送消息
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'王富贵',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,输出回复的消息后,向 周聚财 发送消息
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'周聚财',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,输出回复的消息后,向 刘人勇 发送消息
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'刘人勇',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,就彻底没戏了
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('邓哥命犯天煞孤星,注定孤独终老!!');
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
23
01. Promise基础/2.js
Normal file
23
01. Promise基础/2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
const pro = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('开始百米短跑');
|
||||
const duration = Math.floor(Math.random() * 5000);
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
// 成功
|
||||
resolve(duration); // 将任务从挂起->完成
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,脚扭伤了
|
||||
reject('脚扭伤了!');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, duration);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
pro.then(
|
||||
(data) => {
|
||||
console.log('on yeah! 我跑了', data, '秒');
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
console.log('不好意思,', reason);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
33
01. Promise基础/3.js
Normal file
33
01. Promise基础/3.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
// onFulffiled: 成功后的回调
|
||||
// onRejected: 失败后的回调
|
||||
function sendMessage(name) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
resolve(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
reject(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sendMessage('李建刚').then(
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
console.log('成功!', reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
console.log('失败!', reply);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
206
01. Promise基础/笔记.md
Normal file
206
01. Promise基础/笔记.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
|
||||
> 本节课的任务:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 1. 理解Promise A+规范的基本概念
|
||||
> 2. 学会创建Promise
|
||||
> 3. 学会针对Promise进行后续处理
|
||||
|
||||
# 邓哥的烦恼
|
||||
|
||||
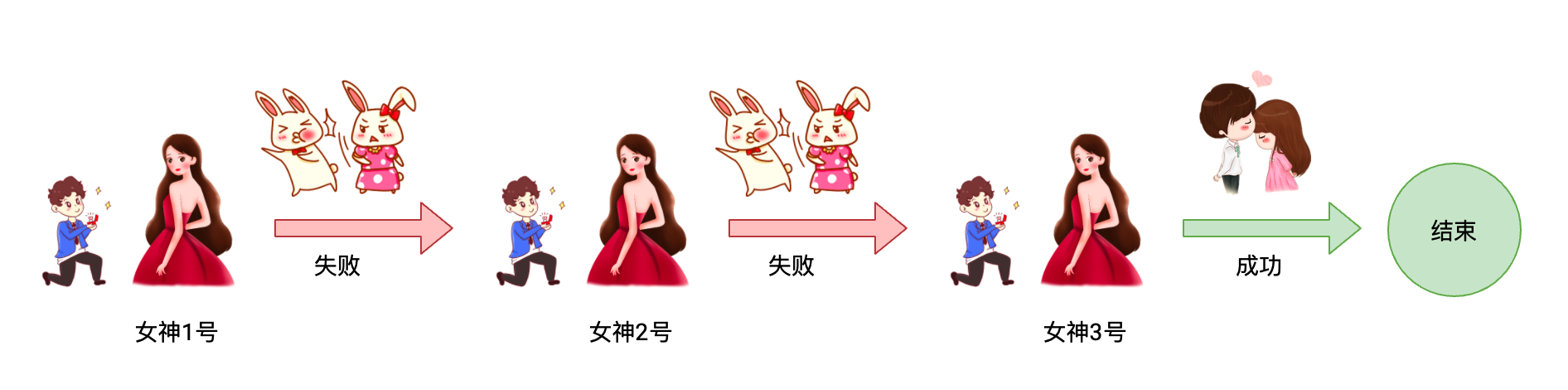
邓哥心中有很多女神,他今天下定决心,要向这些女神表白,他认为,只要女神够多,根据概率学原理,总有一个会接收他
|
||||
|
||||
稳妥起见,邓哥决定使用**串行**的方式进行表白:先给第1位女神发送短信,然后等待女神的回应,如果成功了,就结束,如果失败了,则再给第2位女神发送短信,依次类推
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
邓哥的女神一共有4位,名字分别是:李建国、王富贵、周聚财、刘人勇
|
||||
|
||||
发短信是一个重复性的劳动,邓哥是个程序员,因此决定用函数封装这个动作
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
// onFulffiled: 成功后的回调
|
||||
// onRejected: 失败后的回调
|
||||
function sendMessage(name, onFulffiled, onRejected) {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
onFulffiled(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
onRejected(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有了这个函数后,邓哥于是开始编写程序发送短信了
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 首先向 李建国 发送消息
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'李建国',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,输出回复的消息后,向 王富贵 发送消息
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'王富贵',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,输出回复的消息后,向 周聚财 发送消息
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'周聚财',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,输出回复的消息后,向 刘人勇 发送消息
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
sendMessage(
|
||||
'刘人勇',
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果成功了,输出回复的消息后,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 如果失败了,就彻底没戏了
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('邓哥命犯天煞孤星,注定孤独终老!!');
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该程序完成后,邓哥内心是崩溃的
|
||||
|
||||
这一层一层的回调嵌套,形成了传说中的「**回调地狱 callback hell**」
|
||||
|
||||
邓哥是个完美主义者,怎么能忍受这样的代码呢?
|
||||
|
||||
要解决这样的问题,需要Promise出马
|
||||
|
||||
# Promise规范
|
||||
|
||||
Promise是一套专门处理异步场景的规范,它能有效的避免回调地狱的产生,使异步代码更加清晰、简洁、统一
|
||||
|
||||
这套规范最早诞生于前端社区,规范名称为[Promise A+](https://promisesaplus.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
该规范出现后,立即得到了很多开发者的响应
|
||||
|
||||
Promise A+ 规定:
|
||||
|
||||
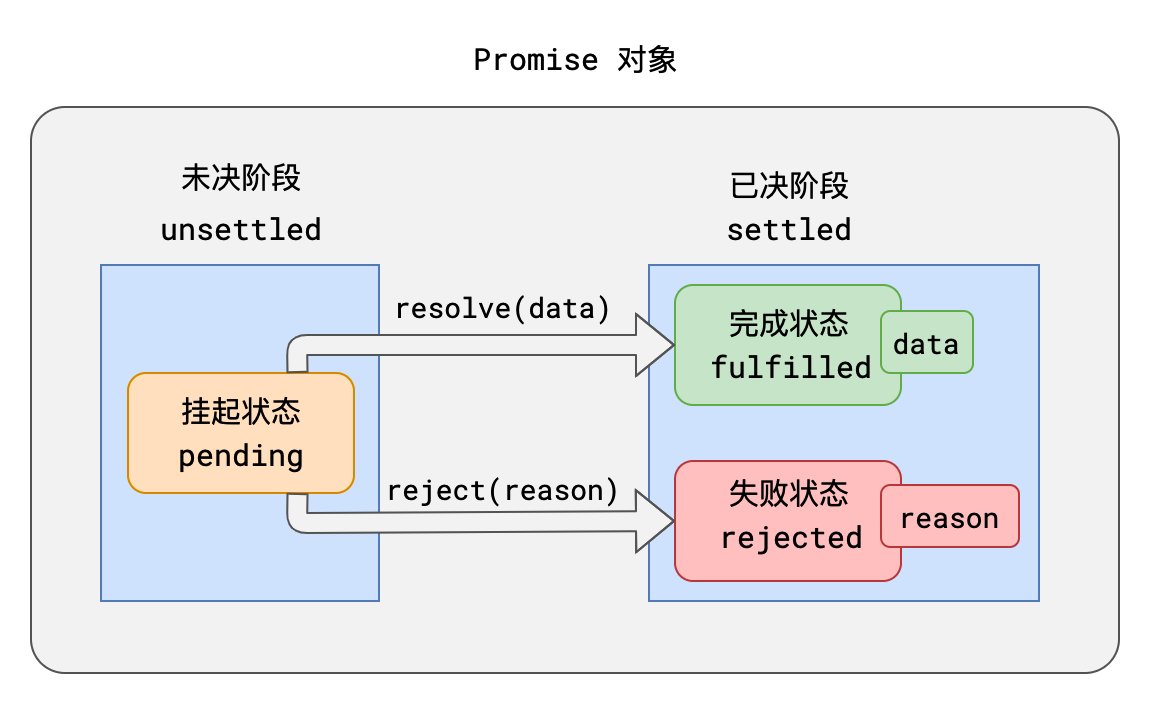
1. 所有的异步场景,都可以看作是一个异步任务,每个异步任务,在JS中应该表现为一个**对象**,该对象称之为**Promise对象**,也叫做任务对象
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="http://mdrs.yuanjin.tech/img/20210618154556.png" alt="image-20210618154556558" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
2. 每个任务对象,都应该有两个阶段、三个状态
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="http://mdrs.yuanjin.tech/img/20210618155145.png" alt="image-20210618155145355" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
根据常理,它们之间存在以下逻辑:
|
||||
|
||||
- 任务总是从未决阶段变到已决阶段,无法逆行
|
||||
- 任务总是从挂起状态变到完成或失败状态,无法逆行
|
||||
- 时间不能倒流,历史不可改写,任务一旦完成或失败,状态就固定下来,永远无法改变
|
||||
|
||||
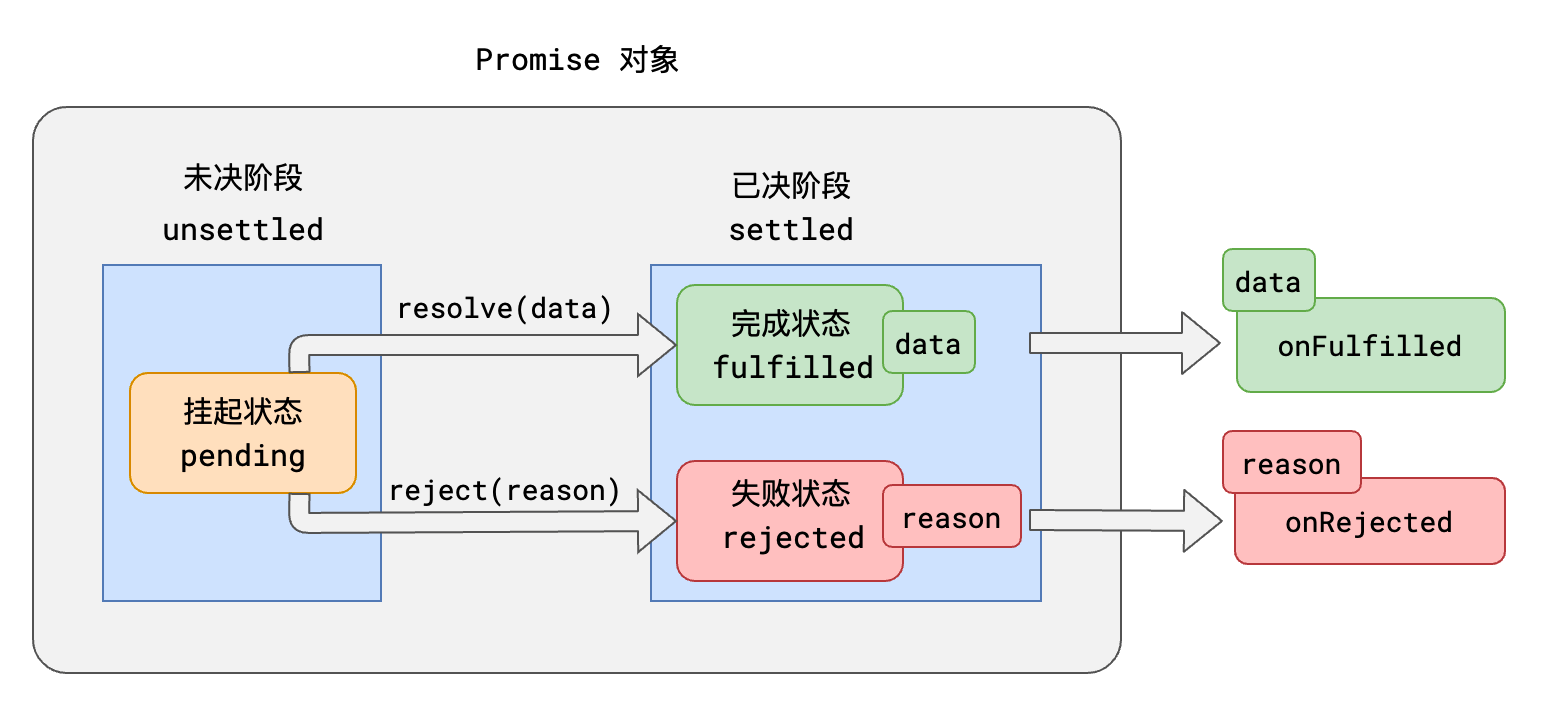
3. `挂起->完成`,称之为`resolve`;`挂起->失败`称之为`reject`。任务完成时,可能有一个相关数据;任务失败时,可能有一个失败原因。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4. 可以针对任务进行后续处理,针对完成状态的后续处理称之为onFulfilled,针对失败的后续处理称之为onRejected
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Promise API
|
||||
|
||||
ES6提供了一套API,实现了Promise A+规范
|
||||
|
||||
基本使用如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 创建一个任务对象,该任务立即进入 pending 状态
|
||||
const pro = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 任务的具体执行流程,该函数会立即被执行
|
||||
// 调用 resolve(data),可将任务变为 fulfilled 状态, data 为需要传递的相关数据
|
||||
// 调用 reject(reason),可将任务变为 rejected 状态,reason 为需要传递的失败原因
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
pro.then(
|
||||
(data) => {
|
||||
// onFulfilled 函数,当任务完成后,会自动运行该函数,data为任务完成的相关数据
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
// onRejected 函数,当任务失败后,会自动运行该函数,reason为任务失败的相关原因
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 邓哥的解决方案
|
||||
|
||||
学习了ES6的Promise后,邓哥决定对`sendMessage`函数进行改造,改造结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
// 该函数返回一个任务对象
|
||||
function sendMessage(name) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 resolve,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
resolve(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 reject,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
reject(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后,就可以使用该函数来发送消息了
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
sendMessage('李建国').then(
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 女神答应了,输出女神的回复
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
// 女神拒绝了,输出女神的回复
|
||||
console.log(reason);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 至此,回调地狱的问题仍然没能解决
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 要解决回调地狱,还需要进一步学习Promise的知识
|
||||
12
01. Promise基础/练习题/p1.js
Normal file
12
01. Promise基础/练习题/p1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
//1. 完成下面的函数
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 延迟一段指定的时间
|
||||
* @param {Number} duration 等待的时间
|
||||
* @returns {Promise} 返回一个任务,该任务在指定的时间后完成
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function delay(duration) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. 按照要求,调用delay函数,完成程序
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用delay函数,等待1秒钟,输出:finish
|
||||
26
01. Promise基础/练习题/p2.html
Normal file
26
01. Promise基础/练习题/p2.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
|
||||
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
|
||||
<title>Document</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div class="container"></div>
|
||||
<p class="label"></p>
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
// 根据指定的图片路径,创建一个img元素
|
||||
// 该函数需要返回一个Promise,当图片加载完成后,任务完成,若图片加载失败,任务失败
|
||||
// 任务完成后,需要提供的数据是图片DOM元素;任务失败时,需要提供失败的原因
|
||||
// 提示:img元素有两个事件,load事件会在图像加载完成时触发,error事件会在图像加载失败时触发
|
||||
function createImage(imgUrl) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// 使用createImage函数创建一个图像,图像路径自行定义
|
||||
// 当图像成功加载后,将图像宽高显示在p元素中,当图像加载失败后,输出加载失败的原因
|
||||
|
||||
// 使用createImage函数创建一个图像,图像路径自行定义
|
||||
// 当图像成功加载后,将图像元素加入到container容器中,当图像加载失败后,输出加载失败的原因
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
28
01. Promise基础/练习题/p3.html
Normal file
28
01. Promise基础/练习题/p3.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
|
||||
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
|
||||
<title>Document</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<select id="selProvince"></select>
|
||||
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
// 你无须知道该函数是如何实现的!!!
|
||||
// 调用该函数,会远程加载省份数据
|
||||
// 函数返回一个Promise,成功后得到省份数组,失败时会给予失败原因
|
||||
function getProvinces() {
|
||||
return fetch('https://study.duyiedu.com/api/citylist')
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.json())
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.data)
|
||||
.then((resp) =>
|
||||
resp.map((it) => ({ value: it.value, label: it.label }))
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用getProvinces函数,将省份数据加载到select元素中
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
16
01. Promise基础/练习题/p4.js
Normal file
16
01. Promise基础/练习题/p4.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
// 下面的任务最终状态是什么,相关的数据或失败原因是什么,最终输出什么
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('任务开始');
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
reject(2);
|
||||
resolve(3);
|
||||
console.log('任务结束');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('任务开始');
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
resolve(2);
|
||||
console.log('任务结束');
|
||||
});
|
||||
21
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p1.js
Normal file
21
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
//1. 完成下面的函数
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 延迟一段指定的时间
|
||||
* @param {Number} duration 等待的时间
|
||||
* @returns {Promise} 返回一个任务,该任务在指定的时间后完成
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function delay(duration) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
}, duration);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. 按照要求,调用delay函数,完成程序
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用delay函数,等待1秒钟,输出:finish
|
||||
delay(1000).then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('finish');
|
||||
});
|
||||
59
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p2.html
Normal file
59
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p2.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
|
||||
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
|
||||
<title>Document</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div class="container"></div>
|
||||
<p class="label"></p>
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
// 根据指定的图片路径,创建一个img元素
|
||||
// 该函数需要返回一个Promise,当图片加载完成后,任务完成,若图片加载失败,任务失败
|
||||
// 任务完成后,需要提供的数据是图片DOM元素;任务失败时,需要提供失败的原因
|
||||
// 提示:img元素有两个事件,load事件会在图像加载完成时触发,error事件会在图像加载失败时触发
|
||||
function createImage(imgUrl) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
const img = document.createElement('img');
|
||||
img.src = imgUrl;
|
||||
img.onload = () => {
|
||||
// 图像加载完成
|
||||
resolve(img);
|
||||
};
|
||||
img.onerror = (e) => {
|
||||
// 图像加载失败
|
||||
reject(e);
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 使用createImage函数创建一个图像,图像路径自行定义
|
||||
// 当图像成功加载后,将图像宽高显示在p元素中,当图像加载失败后,输出加载失败的原因
|
||||
const url1 =
|
||||
'https://dss3.bdstatic.com/70cFv8Sh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=155346741,3953923104&fm=26&gp=0.jpg';
|
||||
createImage(url1).then(
|
||||
(img) => {
|
||||
const p = document.querySelector('.label');
|
||||
p.innerHTML = `${img.width} * ${img.height}`;
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
console.log(reason);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
// 使用createImage函数创建一个图像,图像路径自行定义
|
||||
// 当图像成功加载后,将图像元素加入到container容器中,当图像加载失败后,输出加载失败的原因
|
||||
createImage(url1).then(
|
||||
(img) => {
|
||||
const div = document.querySelector('.container');
|
||||
div.appendChild(img);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
console.log(reason);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
39
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p3.html
Normal file
39
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p3.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
|
||||
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
|
||||
<title>Document</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<select id="selProvince"></select>
|
||||
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
// 你无须知道该函数是如何实现的!!!
|
||||
// 调用该函数,会远程加载省份数据
|
||||
// 函数返回一个Promise,成功后得到省份数组,失败时会给予失败原因
|
||||
function getProvinces() {
|
||||
return fetch('https://study.duyiedu.com/api/citylist')
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.json())
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.data)
|
||||
.then((resp) =>
|
||||
resp.map((it) => ({ value: it.value, label: it.label }))
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 利用getProvinces函数,将省份数据加载到select元素中
|
||||
getProvinces().then(
|
||||
(ps) => {
|
||||
const html = ps
|
||||
.map((p) => `<option value="${p.value}">${p.label}</option>`)
|
||||
.join('');
|
||||
const selProvince = document.getElementById('selProvince');
|
||||
selProvince.innerHTML = html;
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
console.log(reason);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
18
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p4.js
Normal file
18
01. Promise基础/练习题参考答案/p4.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
// 下面的任务最终状态是什么,相关的数据或失败原因是什么,最终输出什么
|
||||
|
||||
const pro1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('任务开始');
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
reject(2); // 无效
|
||||
resolve(3); // 无效
|
||||
console.log('任务结束');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(pro1);
|
||||
|
||||
// new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// console.log('任务开始');
|
||||
// resolve(1);
|
||||
// resolve(2); // 无效
|
||||
// console.log('任务结束');
|
||||
// });
|
||||
5
02. Promise的链式调用/1.js
Normal file
5
02. Promise的链式调用/1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
reject(new Error('abc'));
|
||||
}).catch((err) => {
|
||||
console.log('失败了!!', err);
|
||||
});
|
||||
12
02. Promise的链式调用/2.js
Normal file
12
02. Promise的链式调用/2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
const pro1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('学习');
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const pro2 = pro1.then(() => {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log(pro2);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
52
02. Promise的链式调用/3.js
Normal file
52
02. Promise的链式调用/3.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
// 返回:Promise
|
||||
function sendMessage(name) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.3) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
resolve(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
reject(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sendMessage('李建国')
|
||||
.catch((reply) => {
|
||||
// 失败,继续
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
return sendMessage('王富贵');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((reply) => {
|
||||
// 失败,继续
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
return sendMessage('周聚财');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((reply) => {
|
||||
// 失败,继续
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
return sendMessage('刘人勇');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then(
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 成功,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('邓哥终于找到了自己的伴侣');
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 最后一个也失败了
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('邓哥命犯天煞孤星,无伴终老,孤独一生');
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
103
02. Promise的链式调用/笔记.md
Normal file
103
02. Promise的链式调用/笔记.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# catch方法
|
||||
|
||||
`.catch(onRejected)` = `.then(null, onRejected)`
|
||||
|
||||
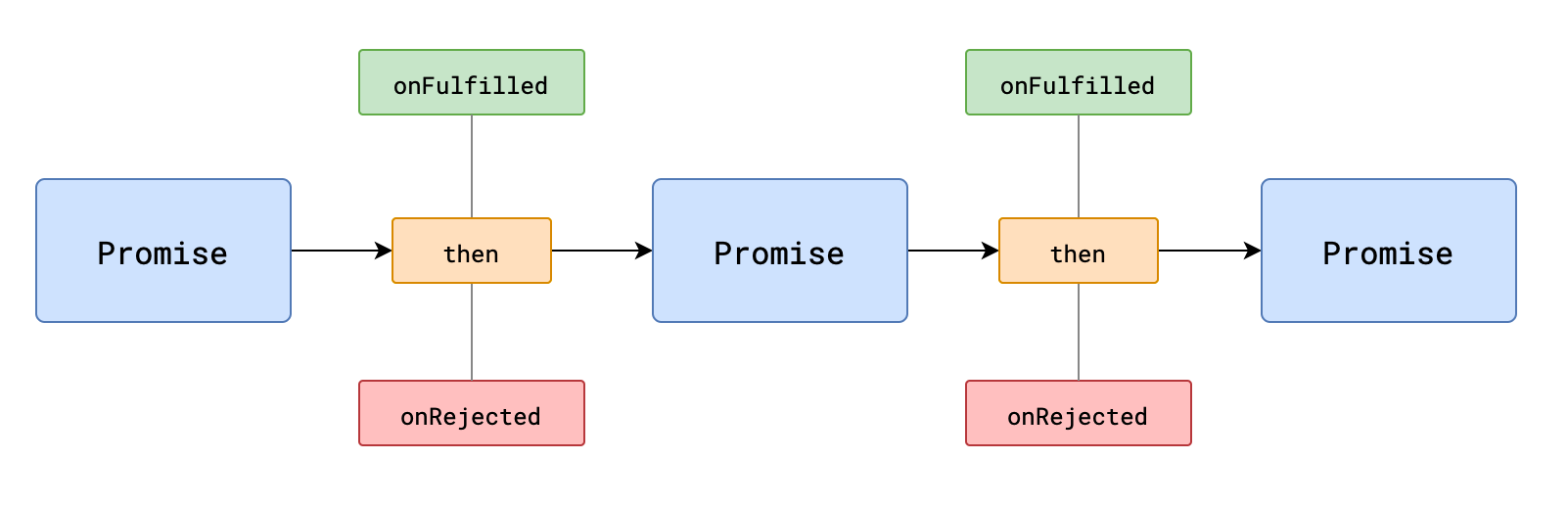
# 链式调用
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. then方法必定会返回一个新的Promise
|
||||
|
||||
可理解为`后续处理也是一个任务`
|
||||
|
||||
2. 新任务的状态取决于后续处理:
|
||||
|
||||
- 若没有相关的后续处理,新任务的状态和前任务一致,数据为前任务的数据
|
||||
|
||||
- 若有后续处理但还未执行,新任务挂起。
|
||||
- 若后续处理执行了,则根据后续处理的情况确定新任务的状态
|
||||
- 后续处理执行无错,新任务的状态为完成,数据为后续处理的返回值
|
||||
- 后续处理执行有错,新任务的状态为失败,数据为异常对象
|
||||
- 后续执行后返回的是一个任务对象,新任务的状态和数据与该任务对象一致
|
||||
|
||||
由于链式任务的存在,异步代码拥有了更强的表达力
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 常见任务处理代码
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* 任务成功后,执行处理1,失败则执行处理2
|
||||
*/
|
||||
pro.then(处理1).catch(处理2)
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* 任务成功后,依次执行处理1、处理2
|
||||
*/
|
||||
pro.then(处理1).then(处理2)
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* 任务成功后,依次执行处理1、处理2,若任务失败或前面的处理有错,执行处理3
|
||||
*/
|
||||
pro.then(处理1).then(处理2).catch(处理3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 邓哥的解决方案
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
// onFulffiled: 成功后的回调
|
||||
// onRejected: 失败后的回调
|
||||
function sendMessage(name) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
resolve(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
reject(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sendMessage('李建国')
|
||||
.catch((reply) => {
|
||||
// 失败,继续
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
return sendMessage('王富贵');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((reply) => {
|
||||
// 失败,继续
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
return sendMessage('周聚财');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((reply) => {
|
||||
// 失败,继续
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
return sendMessage('刘人勇');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then(
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 成功,结束
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('邓哥终于找到了自己的伴侣');
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reply) => {
|
||||
// 最后一个也失败了
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('邓哥命犯天煞孤星,无伴终老,孤独一生');
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
14
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p1.js
Normal file
14
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((data) => {
|
||||
throw 3;
|
||||
return data + 1;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((data) => {
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
});
|
||||
19
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p2.js
Normal file
19
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
const pro = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((err) => {
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log(pro);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
19
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p3.js
Normal file
19
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p3.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
const pro = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res.toString()); // 报错
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((err) => {
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log(pro);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
16
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p4.js
Normal file
16
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p4.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
return new Error('2');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((err) => {
|
||||
throw err;
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
});
|
||||
18
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p5.js
Normal file
18
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题.1/p5.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
// 下面的代码输出什么
|
||||
|
||||
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
reject();
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
const promise2 = promise1.catch(() => {
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1);
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2);
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1);
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2);
|
||||
}, 2000);
|
||||
21
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p1.js
Normal file
21
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
const pro1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const pro2 = pro1.then((data) => {
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
return data + 1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const pro3 = pro2.then((data) => {
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(pro1, pro2, pro3);
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log(pro1, pro2, pro3);
|
||||
}, 2000);
|
||||
15
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p2.js
Normal file
15
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
resolve(1);
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((err) => {
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
});
|
||||
15
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p3.js
Normal file
15
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p3.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res.toString());
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((err) => {
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
});
|
||||
16
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p4.js
Normal file
16
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p4.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
// 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
throw new Error(1);
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
return new Error('2');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.catch((err) => {
|
||||
throw err;
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then((res) => {
|
||||
console.log(res);
|
||||
});
|
||||
18
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p5.js
Normal file
18
02. Promise的链式调用/练习题/p5.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
// 下面的代码输出什么
|
||||
|
||||
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
reject();
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
const promise2 = promise1.catch(() => {
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1);
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2);
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1);
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2);
|
||||
}, 2000);
|
||||
50
03. Promise的静态方法/1.js
Normal file
50
03. Promise的静态方法/1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
// 做饭
|
||||
function cook() {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥打开了电饭煲');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
resolve('饭已ok');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
reject('做饭却忘了加水,米饭变成了爆米花');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 2000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 洗衣服
|
||||
function wash() {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥打开了洗衣机');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
resolve('衣服已经洗好');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
reject('洗衣服时停水了,洗了个寂寞');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 2500);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 打扫卫生
|
||||
function sweep() {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥打开了扫地机器人');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
resolve('地板扫的非常干净');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
reject('扫地机器人被哈士奇一爪掀翻了');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 3000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Promise.allSettled([cook(), wash(), sweep()]).then((result) => {
|
||||
// 处理汇总结果
|
||||
|
||||
const report = result
|
||||
.map((r) => (r.status === 'fulfilled' ? r.value : r.reason))
|
||||
.join(';');
|
||||
console.log(report);
|
||||
});
|
||||
16
03. Promise的静态方法/2.js
Normal file
16
03. Promise的静态方法/2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
// const pro = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// reject(1);
|
||||
// });
|
||||
// console.log(pro);
|
||||
|
||||
const pro = Promise.race([
|
||||
Promise.reject(1),
|
||||
Promise.reject(2),
|
||||
Promise.resolve(3),
|
||||
]);
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log(pro);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
// pro.catch((result) => {
|
||||
// console.log('失败', result.errors);
|
||||
// });
|
||||
95
03. Promise的静态方法/笔记.md
Normal file
95
03. Promise的静态方法/笔记.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
# 邓哥的新问题
|
||||
|
||||
邓嫂出门时,给邓哥交待了几个任务:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 做饭
|
||||
|
||||
可交给电饭煲完成
|
||||
|
||||
2. 洗衣服
|
||||
|
||||
可交给洗衣机完成
|
||||
|
||||
3. 打扫卫生
|
||||
|
||||
可交给扫地机器人完成
|
||||
|
||||
邓哥需要在所有任务结束后给邓嫂汇报工作,哪些成功了,哪些失败了
|
||||
|
||||
为了最大程度的节约时间,邓哥希望这些任务同时进行,最终汇总结果统一处理
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="http://mdrs.yuanjin.tech/img/20210621142519.png" alt="image-20210621142519937" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
每个任务可以看做是一个返回Promise的函数
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 做饭
|
||||
function cook() {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥打开了电饭煲');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
resolve('饭已ok');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
reject('做饭却忘了加水,米饭变成了爆米花');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 2000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 洗衣服
|
||||
function wash() {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥打开了洗衣机');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
resolve('衣服已经洗好');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
reject('洗衣服时停水了,洗了个寂寞');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 2500);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 打扫卫生
|
||||
function sweep() {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥打开了扫地机器人');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
|
||||
resolve('地板扫的非常干净');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
reject('扫地机器人被哈士奇一爪掀翻了');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 3000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如何利用这三个函数实现邓哥的要求呢?
|
||||
|
||||
# Promise的静态方法
|
||||
|
||||
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|
||||
| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Promise.resolve(data) | 直接返回一个完成状态的任务 |
|
||||
| Promise.reject(reason) | 直接返回一个拒绝状态的任务 |
|
||||
| Promise.all(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组全部成功则成功<br />任何一个失败则失败 |
|
||||
| Promise.any(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组任一成功则成功<br />任务全部失败则失败 |
|
||||
| Promise.allSettled(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组全部已决则成功<br />该任务不会失败 |
|
||||
| Promise.race(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组任一已决则已决,状态和其一致 |
|
||||
| | |
|
||||
|
||||
# 邓哥的解决方案
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
Promise.allSettled([cook(), wash(), sweep()]).then((result) => {
|
||||
// 处理汇总结果
|
||||
const report = result
|
||||
.map((r) => (r.status === 'fulfilled' ? r.value : r.reason))
|
||||
.join(';');
|
||||
console.log(report);
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
30
03. Promise的静态方法/练习题/p1.js
Normal file
30
03. Promise的静态方法/练习题/p1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 根据页码获取学生数据,返回Promise
|
||||
* @param {Number} page 页码
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function fetchStudents(page) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.3) {
|
||||
reject(new Error(`网络错误!获取第${page}页数据失败!`));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 模拟学生数据
|
||||
const stus = new Array(10).fill(null).map((d, i) => ({
|
||||
id: `NO.${(page - 1) * 10 + i + 1}`,
|
||||
name: `姓名${(page - 1) * 10 + i + 1}`,
|
||||
}));
|
||||
resolve(stus);
|
||||
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 5000));
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用 fetchStudents 函数,完成下面的练习
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,最终按照页码的顺序合并成一个数组,任何一页的数据获取出现错误,则任务不再继续,打印错误消息
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,最终按照页码的顺序合并成一个数组,如果某些页码的数据获取失败,就不加入该数据即可
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,打印最先获取到的数据,如果全部都获取失败,则打印所有的错误消息
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,输出最先得到的结果(有结果输出结果,有错误输出错误)
|
||||
12
03. Promise的静态方法/练习题参考答案/p1.html
Normal file
12
03. Promise的静态方法/练习题参考答案/p1.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
|
||||
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
|
||||
<title>Document</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<script src="./p1.js"></script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
62
03. Promise的静态方法/练习题参考答案/p1.js
Normal file
62
03. Promise的静态方法/练习题参考答案/p1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 根据页码获取学生数据,返回Promise
|
||||
* @param {Number} page 页码
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function fetchStudents(page) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
if (Math.random() < 0.3) {
|
||||
reject(new Error(`网络错误!获取第${page}页数据失败!`));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 模拟学生数据
|
||||
const stus = new Array(10).fill(null).map((d, i) => ({
|
||||
id: `NO.${(page - 1) * 10 + i + 1}`,
|
||||
name: `姓名${(page - 1) * 10 + i + 1}`,
|
||||
}));
|
||||
resolve(stus);
|
||||
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 5000));
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用 fetchStudents 函数,完成下面的练习
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,最终按照页码的顺序合并成一个数组,任何一页的数据获取出现错误,则任务不再继续,打印错误消息
|
||||
|
||||
const proms = new Array(10).fill(1).map((it, i) => fetchStudents(i + 1));
|
||||
|
||||
// Promise.all(proms)
|
||||
// .then((result) => {
|
||||
// console.log(result.flat());
|
||||
// })
|
||||
// .catch((err) => {
|
||||
// console.log(err);
|
||||
// });
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,最终按照页码的顺序合并成一个数组,如果某些页码的数据获取失败,就不加入该数据即可
|
||||
// Promise.allSettled(proms).then((result) => {
|
||||
// result = result
|
||||
// .filter((r) => r.status === 'fulfilled')
|
||||
// .map((it) => it.value)
|
||||
// .flat();
|
||||
// console.log(result);
|
||||
// });
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,打印最先获取到的数据,如果全部都获取失败,则打印所有的错误消息
|
||||
// Promise.any(proms)
|
||||
// .then((result) => {
|
||||
// console.log(result);
|
||||
// })
|
||||
// .catch((err) => {
|
||||
// console.log(err.errors);
|
||||
// });
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取1-10页的学生,输出最先得到的结果(有结果输出结果,有错误输出错误)
|
||||
Promise.race(proms).then(
|
||||
(result) => {
|
||||
console.log(result);
|
||||
},
|
||||
(err) => {
|
||||
console.log(err);
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
29
04. async和await/1.js
Normal file
29
04. async和await/1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
function delay(duration) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
reject();
|
||||
}, duration);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// delay(1000).then(() => {
|
||||
// console.log('执行某个东西');
|
||||
// });
|
||||
|
||||
(async () => {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
await delay(1000);
|
||||
console.log('成功');
|
||||
} catch (err) {
|
||||
console.log('失败');
|
||||
}
|
||||
})();
|
||||
|
||||
// delay(1000).then(
|
||||
// (data) => {
|
||||
// console.log('成功');
|
||||
// },
|
||||
// (err) => {
|
||||
// console.log('失败');
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// );
|
||||
45
04. async和await/2.js
Normal file
45
04. async和await/2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
// 女神的名字数组
|
||||
const beautyGirls = ['梁平', '邱杰'];
|
||||
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
function sendMessage(name) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
resolve(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
reject(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async () => {
|
||||
let isSuccess = false;
|
||||
for (const name of beautyGirls) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const reply = await sendMessage(name);
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('表白成功!');
|
||||
isSuccess = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} catch (reply) {
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('表白失败');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isSuccess) {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥注定孤独一生');
|
||||
}
|
||||
})();
|
||||
177
04. async和await/笔记.md
Normal file
177
04. async和await/笔记.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 消除回调
|
||||
|
||||
有了Promise,异步任务就有了一种统一的处理方式
|
||||
|
||||
有了统一的处理方式,ES官方就可以对其进一步优化
|
||||
|
||||
ES7推出了两个关键字`async`和`await`,用于更加优雅的表达Promise
|
||||
|
||||
## async
|
||||
|
||||
async关键字用于修饰函数,被它修饰的函数,一定返回Promise
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method1(){
|
||||
return 1; // 该函数的返回值是Promise完成后的数据
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method1(); // Promise { 1 }
|
||||
|
||||
async function method2(){
|
||||
return Promise.resolve(1); // 若返回的是Promise,则method得到的Promise状态和其一致
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method2(); // Promise { 1 }
|
||||
|
||||
async function method3(){
|
||||
throw new Error(1); // 若执行过程报错,则任务是rejected
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method3(); // Promise { <rejected> Error(1) }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## await
|
||||
|
||||
`await`关键字表示等待某个Promise完成,**它必须用于`async`函数中**
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method(){
|
||||
const n = await Promise.resolve(1);
|
||||
console.log(n); // 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 上面的函数等同于
|
||||
function method(){
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
|
||||
Promise.resolve(1).then(n=>{
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
resolve(1)
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`await`也可以等待其他数据
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method(){
|
||||
const n = await 1; // 等同于 await Promise.resolve(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要针对失败的任务进行处理,可以使用`try-catch`语法
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method(){
|
||||
try{
|
||||
const n = await Promise.reject(123); // 这句代码将抛出异常
|
||||
console.log('成功', n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
catch(err){
|
||||
console.log('失败', err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method(); // 输出: 失败 123
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 邓哥表白的完美解决方案
|
||||
|
||||
邓哥的女神可不是只有4位,而是40位!
|
||||
|
||||
为了更加方便的编写表白代码,邓哥决定把这40位女神放到一个数组中,然后利用async和await轻松完成代码
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 女神的名字数组
|
||||
const beautyGirls = [
|
||||
'梁平',
|
||||
'邱杰',
|
||||
'王超',
|
||||
'冯秀兰',
|
||||
'赖军',
|
||||
'顾强',
|
||||
'戴敏',
|
||||
'吕涛',
|
||||
'冯静',
|
||||
'蔡明',
|
||||
'廖磊',
|
||||
'冯洋',
|
||||
'韩杰',
|
||||
'江涛',
|
||||
'文艳',
|
||||
'杜秀英',
|
||||
'丁艳',
|
||||
'邓静',
|
||||
'江刚',
|
||||
'乔刚',
|
||||
'史平',
|
||||
'康娜',
|
||||
'袁磊',
|
||||
'龙秀英',
|
||||
'姚静',
|
||||
'潘娜',
|
||||
'萧磊',
|
||||
'邵勇',
|
||||
'李芳',
|
||||
'谭芳',
|
||||
'夏秀英',
|
||||
'程娜',
|
||||
'武杰',
|
||||
'崔军',
|
||||
'廖勇',
|
||||
'崔强',
|
||||
'康秀英',
|
||||
'余磊',
|
||||
'邵勇',
|
||||
'贺涛',
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
// 向某位女生发送一则表白短信
|
||||
// name: 女神的姓名
|
||||
function sendMessage(name) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
// 模拟 发送表白短信
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`邓哥 -> ${name}:最近有谣言说我喜欢你,我要澄清一下,那不是谣言😘`
|
||||
);
|
||||
console.log(`等待${name}回复......`);
|
||||
// 模拟 女神回复需要一段时间
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
// 模拟 有10%的几率成功
|
||||
if (Math.random() <= 0.1) {
|
||||
// 成功,调用 onFuffiled,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
resolve(`${name} -> 邓哥:我是九,你是三,除了你还是你😘`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 失败,调用 onRejected,并传递女神的回复
|
||||
reject(`${name} -> 邓哥:你是个好人😜`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 批量表白的程序
|
||||
async function proposal() {
|
||||
let isSuccess = false;
|
||||
for (const girl of beautyGirls) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const reply = await sendMessage(girl);
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('表白成功!');
|
||||
isSuccess = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} catch (reply) {
|
||||
console.log(reply);
|
||||
console.log('表白失败');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!isSuccess) {
|
||||
console.log('邓哥注定孤独一生');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
proposal();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
13
04. async和await/练习题/p1.html
Normal file
13
04. async和await/练习题/p1.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
<ul id="heroList"></ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 远程获取王者荣耀所有的英雄数据
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function getHeroes() {
|
||||
return fetch('https://study.duyiedu.com/api/herolist')
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.json())
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.data);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 利用getHeroes方法,获取所有的英雄数据,将英雄名称显示到页面的列表中
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
7
04. async和await/练习题/p2.js
Normal file
7
04. async和await/练习题/p2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
// 完成delay函数
|
||||
// 该函数可以等待一段指定的时间
|
||||
// 返回Promise
|
||||
function delay(duration) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用delay函数,等待3次,每次等待1秒,每次等待完成后输出ok
|
||||
// 等待1秒->ok->等待1秒->ok->等待1秒->ok
|
||||
19
04. async和await/练习题参考答案/p1.html
Normal file
19
04. async和await/练习题参考答案/p1.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
<ul id="heroList"></ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 远程获取王者荣耀所有的英雄数据
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function getHeroes() {
|
||||
return fetch('https://study.duyiedu.com/api/herolist')
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.json())
|
||||
.then((resp) => resp.data);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 利用getHeroes方法,获取所有的英雄数据,将英雄名称显示到页面的列表中
|
||||
const ul = document.getElementById('heroList');
|
||||
(async () => {
|
||||
const data = await getHeroes();
|
||||
const result = data.map((d) => `<li>${d.cname}</li>`).join('');
|
||||
ul.innerHTML = result;
|
||||
})();
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
33
04. async和await/练习题参考答案/p2.js
Normal file
33
04. async和await/练习题参考答案/p2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
// 完成delay函数
|
||||
// 该函数可以等待一段指定的时间
|
||||
// 返回Promise
|
||||
function delay(duration) {
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
}, duration);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 利用delay函数,等待3次,每次等待1秒,每次等待完成后输出ok
|
||||
// 等待1秒->ok->等待1秒->ok->等待1秒->ok
|
||||
|
||||
(async () => {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
|
||||
await delay(1000);
|
||||
console.log('ok');
|
||||
}
|
||||
})();
|
||||
|
||||
// delay(1000)
|
||||
// .then(() => {
|
||||
// console.log('ok');
|
||||
// return delay(1000);
|
||||
// })
|
||||
// .then(() => {
|
||||
// console.log('ok');
|
||||
// return delay(1000);
|
||||
// })
|
||||
// .then(() => {
|
||||
// console.log('ok');
|
||||
// });
|
||||
11
05. Promise相关面试题/1.js
Normal file
11
05. Promise相关面试题/1.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log(1);
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
promise.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log(3);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(4);
|
||||
14
05. Promise相关面试题/2.js
Normal file
14
05. Promise相关面试题/2.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log(1);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
promise.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log(3);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(4);
|
||||
16
05. Promise相关面试题/3.js
Normal file
16
05. Promise相关面试题/3.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
reject();
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
});
|
||||
const promise2 = promise1.catch(() => {
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1);
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2);
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1);
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2);
|
||||
}, 2000);
|
||||
14
05. Promise相关面试题/4.js
Normal file
14
05. Promise相关面试题/4.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
async function m() {
|
||||
console.log(0);
|
||||
const n = await 1;
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// function m() {
|
||||
// return Promise.resolve(1).then((n) => {
|
||||
// console.log(n);
|
||||
// });
|
||||
// }
|
||||
|
||||
m();
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
12
05. Promise相关面试题/5.js
Normal file
12
05. Promise相关面试题/5.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
async function m() {
|
||||
console.log(0);
|
||||
const n = await 1;
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async () => {
|
||||
await m();
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
})();
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(3);
|
||||
23
05. Promise相关面试题/6.js
Normal file
23
05. Promise相关面试题/6.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
async function m1() {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function m2() {
|
||||
const n = await m1();
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function m3() {
|
||||
const n = m2();
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m3().then((n) => {
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
m3();
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(4);
|
||||
1
05. Promise相关面试题/7.js
Normal file
1
05. Promise相关面试题/7.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
Promise.resolve(1).then(2).then(Promise.resolve(3)).then(console.log);
|
||||
28
05. Promise相关面试题/8.js
Normal file
28
05. Promise相关面试题/8.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
var a;
|
||||
var b = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('promise1');
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise2');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise3');
|
||||
})
|
||||
.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise4');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
a = new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log(a);
|
||||
await b;
|
||||
console.log(a);
|
||||
console.log('after1');
|
||||
await a;
|
||||
resolve(true);
|
||||
console.log('after2');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('end');
|
||||
24
05. Promise相关面试题/9.js
Normal file
24
05. Promise相关面试题/9.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
async function async1() {
|
||||
console.log('async1 start');
|
||||
await async2();
|
||||
console.log('async1 end');
|
||||
}
|
||||
async function async2() {
|
||||
console.log('async2');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('script start');
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(function () {
|
||||
console.log('setTimeout');
|
||||
}, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
async1();
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise(function (resolve) {
|
||||
console.log('promise1');
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
}).then(function () {
|
||||
console.log('promise2');
|
||||
});
|
||||
console.log('script end');
|
||||
311
05. Promise相关面试题/笔记.md
Normal file
311
05. Promise相关面试题/笔记.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,311 @@
|
||||
# 面试题考点
|
||||
|
||||
## Promise的基本概念
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 链式调用规则
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. then方法必定会返回一个新的Promise
|
||||
|
||||
可理解为`后续处理也是一个任务`
|
||||
|
||||
2. 新任务的状态取决于后续处理:
|
||||
|
||||
- 若没有相关的后续处理,新任务的状态和前任务一致,数据为前任务的数据
|
||||
|
||||
- 若有后续处理但还未执行,新任务挂起。
|
||||
- 若后续处理执行了,则根据后续处理的情况确定新任务的状态
|
||||
- 后续处理执行无错,新任务的状态为完成,数据为后续处理的返回值
|
||||
- 后续处理执行有错,新任务的状态为失败,数据为异常对象
|
||||
- 后续执行后返回的是一个任务对象,新任务的状态和数据与该任务对象一致
|
||||
|
||||
## Promise的静态方法
|
||||
|
||||
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|
||||
| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Promise.resolve(data) | 直接返回一个完成状态的任务 |
|
||||
| Promise.reject(reason) | 直接返回一个拒绝状态的任务 |
|
||||
| Promise.all(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组全部成功则成功<br />任何一个失败则失败 |
|
||||
| Promise.any(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组任一成功则成功<br />任务全部失败则失败 |
|
||||
| Promise.allSettled(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组全部已决则成功<br />该任务不会失败 |
|
||||
| Promise.race(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组任一已决则已决,状态和其一致 |
|
||||
| | |
|
||||
|
||||
## async和await
|
||||
|
||||
有了Promise,异步任务就有了一种统一的处理方式
|
||||
|
||||
有了统一的处理方式,ES官方就可以对其进一步优化
|
||||
|
||||
ES7推出了两个关键字`async`和`await`,用于更加优雅的表达Promise
|
||||
|
||||
### async
|
||||
|
||||
async关键字用于修饰函数,被它修饰的函数,一定返回Promise
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method1(){
|
||||
return 1; // 该函数的返回值是Promise完成后的数据
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method1(); // Promise { 1 }
|
||||
|
||||
async function method2(){
|
||||
return Promise.resolve(1); // 若返回的是Promise,则method得到的Promise状态和其一致
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method2(); // Promise { 1 }
|
||||
|
||||
async function method3(){
|
||||
throw new Error(1); // 若执行过程报错,则任务是rejected
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method3(); // Promise { <rejected> Error(1) }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### await
|
||||
|
||||
`await`关键字表示等待某个Promise完成,**它必须用于`async`函数中**
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method(){
|
||||
const n = await Promise.resolve(1);
|
||||
console.log(n); // 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 上面的函数等同于
|
||||
function method(){
|
||||
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
|
||||
Promise.resolve(1).then(n=>{
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
resolve(1)
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`await`也可以等待其他数据
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method(){
|
||||
const n = await 1; // 等同于 await Promise.resolve(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要针对失败的任务进行处理,可以使用`try-catch`语法
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function method(){
|
||||
try{
|
||||
const n = await Promise.reject(123); // 这句代码将抛出异常
|
||||
console.log('成功', n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
catch(err){
|
||||
console.log('失败', err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
method(); // 输出: 失败 123
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 事件循环
|
||||
|
||||
根据目前所学,进入事件队列的函数有以下几种:
|
||||
|
||||
- `setTimeout`的回调,宏任务(macro task)
|
||||
- `setInterval`的回调,宏任务(macro task)
|
||||
- Promise的`then`函数回调,**微任务**(micro task)
|
||||
- `requestAnimationFrame`的回调,宏任务(macro task)
|
||||
- 事件处理函数,宏任务(macro task)
|
||||
|
||||
# 面试题
|
||||
|
||||
1. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log(1);
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
promise.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log(3);
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(4);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log(1);
|
||||
setTimeout(()=>{
|
||||
console.log(2)
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
console.log(3);
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
promise.then(() => {
|
||||
console.log(4);
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(5);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
resolve()
|
||||
}, 1000)
|
||||
})
|
||||
const promise2 = promise1.catch(() => {
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1)
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2)
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise1', promise1)
|
||||
console.log('promise2', promise2)
|
||||
}, 2000)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function m(){
|
||||
const n = await 1;
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m();
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function m(){
|
||||
const n = await 1;
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async ()=>{
|
||||
await m();
|
||||
console.log(2);
|
||||
})();
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(3);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
6. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function m1(){
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function m2(){
|
||||
const n = await m1();
|
||||
console.log(n)
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function m3(){
|
||||
const n = m2();
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m3().then(n=>{
|
||||
console.log(n);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
m3();
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(4);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
Promise.resolve(1)
|
||||
.then(2)
|
||||
.then(Promise.resolve(3))
|
||||
.then(console.log)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var a;
|
||||
var b = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log('promise1');
|
||||
setTimeout(()=>{
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
}).then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise2');
|
||||
}).then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise3');
|
||||
}).then(() => {
|
||||
console.log('promise4');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
a = new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
console.log(a);
|
||||
await b;
|
||||
console.log(a);
|
||||
console.log('after1');
|
||||
await a
|
||||
resolve(true);
|
||||
console.log('after2');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('end');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
async function async1() {
|
||||
console.log('async1 start');
|
||||
await async2();
|
||||
console.log('async1 end');
|
||||
}
|
||||
async function async2() {
|
||||
console.log('async2');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('script start');
|
||||
|
||||
setTimeout(function() {
|
||||
console.log('setTimeout');
|
||||
}, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
async1();
|
||||
|
||||
new Promise(function(resolve) {
|
||||
console.log('promise1');
|
||||
resolve();
|
||||
}).then(function() {
|
||||
console.log('promise2');
|
||||
});
|
||||
console.log('script end');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
287
06. 手写Promise/MyPromise.js
Normal file
287
06. 手写Promise/MyPromise.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,287 @@
|
||||
// 记录Promise的三种状态
|
||||
const PENDING = 'pending';
|
||||
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
|
||||
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 运行一个微队列任务
|
||||
* 把传递的函数放到微队列中
|
||||
* @param {Function} callback
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function runMicroTask(callback) {
|
||||
// 判断node环境
|
||||
// 为了避免「变量未定义」的错误,这里最好加上前缀globalThis
|
||||
// globalThis是一个关键字,指代全局对象,浏览器环境为window,node环境为global
|
||||
if (globalThis.process && globalThis.process.nextTick) {
|
||||
process.nextTick(callback);
|
||||
} else if (globalThis.MutationObserver) {
|
||||
const p = document.createElement('p');
|
||||
const observer = new MutationObserver(callback);
|
||||
observer.observe(p, {
|
||||
childList: true, // 观察该元素内部的变化
|
||||
});
|
||||
p.innerHTML = '1';
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
setTimeout(callback, 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 判断一个数据是否是Promise对象
|
||||
* @param {any} obj
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function isPromise(obj) {
|
||||
return !!(obj && typeof obj === 'object' && typeof obj.then === 'function');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
class MyPromise {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 创建一个Promise
|
||||
* @param {Function} executor 任务执行器,立即执行
|
||||
*/
|
||||
constructor(executor) {
|
||||
this._state = PENDING; // 状态
|
||||
this._value = undefined; // 数据
|
||||
this._handlers = []; // 处理函数形成的队列
|
||||
try {
|
||||
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
this._reject(error);
|
||||
console.error(error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 向处理队列中添加一个函数
|
||||
* @param {Function} executor 添加的函数
|
||||
* @param {String} state 该函数什么状态下执行
|
||||
* @param {Function} resolve 让then函数返回的Promise成功
|
||||
* @param {Function} reject 让then函数返回的Promise失败
|
||||
*/
|
||||
_pushHandler(executor, state, resolve, reject) {
|
||||
this._handlers.push({
|
||||
executor,
|
||||
state,
|
||||
resolve,
|
||||
reject,
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 根据实际情况,执行队列
|
||||
*/
|
||||
_runHandlers() {
|
||||
if (this._state === PENDING) {
|
||||
// 目前任务仍在挂起
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (this._handlers[0]) {
|
||||
const handler = this._handlers[0];
|
||||
this._runOneHandler(handler);
|
||||
this._handlers.shift();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 处理一个handler
|
||||
* @param {Object} handler
|
||||
*/
|
||||
_runOneHandler({ executor, state, resolve, reject }) {
|
||||
runMicroTask(() => {
|
||||
if (this._state !== state) {
|
||||
// 状态不一致,不处理
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (typeof executor !== 'function') {
|
||||
// 传递后续处理并非一个函数
|
||||
this._state === FULFILLED ? resolve(this._value) : reject(this._value);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const result = executor(this._value);
|
||||
if (isPromise(result)) {
|
||||
result.then(resolve, reject);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
resolve(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
reject(error);
|
||||
console.error(error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Promise A+规范的then
|
||||
* @param {Function} onFulfilled
|
||||
* @param {Function} onRejected
|
||||
*/
|
||||
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
|
||||
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
this._pushHandler(onFulfilled, FULFILLED, resolve, reject);
|
||||
this._pushHandler(onRejected, REJECTED, resolve, reject);
|
||||
this._runHandlers(); // 执行队列
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 仅处理失败的场景
|
||||
* @param {Function} onRejected
|
||||
*/
|
||||
catch(onRejected) {
|
||||
return this.then(null, onRejected);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 无论成功还是失败都会执行回调
|
||||
* @param {Function} onSettled
|
||||
*/
|
||||
finally(onSettled) {
|
||||
return this.then(
|
||||
(data) => {
|
||||
onSettled();
|
||||
return data;
|
||||
},
|
||||
(reason) => {
|
||||
onSettled();
|
||||
throw reason;
|
||||
}
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 更改任务状态
|
||||
* @param {String} newState 新状态
|
||||
* @param {any} value 相关数据
|
||||
*/
|
||||
_changeState(newState, value) {
|
||||
if (this._state !== PENDING) {
|
||||
// 目前状态已经更改
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
this._state = newState;
|
||||
this._value = value;
|
||||
this._runHandlers(); // 状态变化,执行队列
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 标记当前任务完成
|
||||
* @param {any} data 任务完成的相关数据
|
||||
*/
|
||||
_resolve(data) {
|
||||
this._changeState(FULFILLED, data);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 标记当前任务失败
|
||||
* @param {any} reason 任务失败的相关数据
|
||||
*/
|
||||
_reject(reason) {
|
||||
this._changeState(REJECTED, reason);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 返回一个已完成的Promise
|
||||
* 特殊情况:
|
||||
* 1. 传递的data本身就是ES6的Promise对象
|
||||
* 2. 传递的data是PromiseLike(Promise A+),返回新的Promise,状态和其保持一致即可
|
||||
* @param {any} data
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static resolve(data) {
|
||||
if (data instanceof MyPromise) {
|
||||
return data;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
if (isPromise(data)) {
|
||||
data.then(resolve, reject);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
resolve(data);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 得到一个被拒绝的Promise
|
||||
* @param {any}} reason
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static reject(reason) {
|
||||
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
reject(reason);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 得到一个新的Promise
|
||||
* 该Promise的状态取决于proms的执行
|
||||
* proms是一个迭代器,包含多个Promise
|
||||
* 全部Promise成功,则返回的Promise成功,数据为所有Promise成功的数据,并且顺序是按照传入的顺序排列
|
||||
* 只要有一个Promise失败,则返回的Promise失败,原因是第一个失败的Promise的原因
|
||||
* @param {iterator} proms
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static all(proms) {
|
||||
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const results = [];
|
||||
let count = 0; // Promise的总数
|
||||
let fulfilledCount = 0; // 已完成的数量
|
||||
for (const p of proms) {
|
||||
let i = count;
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
MyPromise.resolve(p).then((data) => {
|
||||
fulfilledCount++;
|
||||
results[i] = data;
|
||||
if (fulfilledCount === count) {
|
||||
// 当前是最后一个Promise完成了
|
||||
resolve(results);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, reject);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (count === 0) {
|
||||
resolve(results);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
reject(error);
|
||||
console.error(error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 等待所有的Promise有结果之后
|
||||
* 该方法返回的Promise完成
|
||||
* 并且按照顺序将所有结果汇总
|
||||
* @param {iterator} proms
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static allSettled(proms) {
|
||||
const ps = [];
|
||||
for (const p of proms) {
|
||||
ps.push(
|
||||
MyPromise.resolve(p).then(
|
||||
(value) => ({
|
||||
status: FULFILLED,
|
||||
value,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
(reason) => ({
|
||||
status: REJECTED,
|
||||
reason,
|
||||
})
|
||||
)
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return MyPromise.all(ps);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 返回的Promise与第一个有结果的一致
|
||||
* @param {iterator} proms
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static race(proms) {
|
||||
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
for (const p of proms) {
|
||||
MyPromise.resolve(p).then(resolve, reject);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
3
06. 手写Promise/说明.md
Normal file
3
06. 手写Promise/说明.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
手写 Promise 课程资料,仅提供最终的完整代码
|
||||
|
||||
至于每节课的代码,请同学们理解视频课程内容,然后自行手写,以达到最好的学习效果
|
||||
64
知识图谱.drawio
Normal file
64
知识图谱.drawio
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
<mxfile host="65bd71144e">
|
||||
<diagram id="QFoU5hE6jV3CWI5dNyLY" name="第 1 页">
|
||||
<mxGraphModel dx="685" dy="637" grid="0" gridSize="10" guides="1" tooltips="1" connect="1" arrows="1" fold="1" page="1" pageScale="1" pageWidth="1654" pageHeight="1169" math="0" shadow="0">
|
||||
<root>
|
||||
<mxCell id="0"/>
|
||||
<mxCell id="1" parent="0"/>
|
||||
<mxCell id="19" value="" style="group" parent="1" vertex="1" connectable="0">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="1398" y="116" width="169" height="179" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="16" value="" style="rounded=0;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;fontSize=16;fillColor=#f5f5f5;strokeColor=#666666;fontColor=#333333;" parent="19" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry width="169" height="179" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="3" value="图例" style="text;html=1;align=center;verticalAlign=middle;resizable=0;points=[];autosize=1;strokeColor=none;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;" parent="19" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="63.5" y="7" width="42" height="23" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="4" value="必会知识" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#d5e8d4;strokeColor=#82b366;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;" parent="19" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="18" y="42" width="133" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="5" value="建议学习的知识" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#dae8fc;strokeColor=#6c8ebf;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;" parent="19" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="18" y="85" width="133" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="6" value="选择学习的知识" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#f8cecc;strokeColor=#b85450;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;" parent="19" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="18" y="128" width="133" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="91" value="01. Promise基础" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#d5e8d4;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;strokeColor=#82b366;" parent="1" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="966" y="108" width="237" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="102" value="网络性能优化" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#dae8fc;strokeColor=#6c8ebf;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;" parent="1" vertex="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="582" y="734" width="251" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="157" style="edgeStyle=orthogonalEdgeStyle;rounded=0;orthogonalLoop=1;jettySize=auto;html=1;entryX=0.5;entryY=1;entryDx=0;entryDy=0;" edge="1" parent="1" source="152" target="91">
|
||||
<mxGeometry relative="1" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="152" value="02. Promise的链式调用" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#d5e8d4;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;strokeColor=#82b366;" vertex="1" parent="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="966" y="167" width="237" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="158" style="edgeStyle=orthogonalEdgeStyle;rounded=0;orthogonalLoop=1;jettySize=auto;html=1;entryX=0.5;entryY=1;entryDx=0;entryDy=0;" edge="1" parent="1" source="153" target="152">
|
||||
<mxGeometry relative="1" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="153" value="03. Promise的静态方法" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#d5e8d4;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;strokeColor=#82b366;" vertex="1" parent="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="966" y="226" width="237" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="159" style="edgeStyle=orthogonalEdgeStyle;rounded=0;orthogonalLoop=1;jettySize=auto;html=1;entryX=0.5;entryY=1;entryDx=0;entryDy=0;" edge="1" parent="1" source="154" target="153">
|
||||
<mxGeometry relative="1" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="154" value="04. async 和 await" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#d5e8d4;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;strokeColor=#82b366;" vertex="1" parent="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="966" y="285" width="238" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="160" style="edgeStyle=orthogonalEdgeStyle;rounded=0;orthogonalLoop=1;jettySize=auto;html=1;entryX=0.5;entryY=1;entryDx=0;entryDy=0;" edge="1" parent="1" source="155" target="154">
|
||||
<mxGeometry relative="1" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="155" value="05. Promise的相关面试题" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#d5e8d4;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;strokeColor=#82b366;" vertex="1" parent="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="966" y="344" width="238" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="161" style="edgeStyle=orthogonalEdgeStyle;rounded=0;orthogonalLoop=1;jettySize=auto;html=1;entryX=0.5;entryY=1;entryDx=0;entryDy=0;" edge="1" parent="1" source="156" target="155">
|
||||
<mxGeometry relative="1" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
<mxCell id="156" value="06. 手写Promise(多节课)" style="rounded=1;whiteSpace=wrap;html=1;fillColor=#f8cecc;fontSize=16;fontFamily=Roboto Mono;strokeColor=#b85450;" vertex="1" parent="1">
|
||||
<mxGeometry x="966" y="403" width="238" height="31" as="geometry"/>
|
||||
</mxCell>
|
||||
</root>
|
||||
</mxGraphModel>
|
||||
</diagram>
|
||||
</mxfile>
|
||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user