update hook answer
This commit is contained in:
parent
46dce38662
commit
9de138917c
@ -1,354 +1,366 @@
|
|||||||
# effect相关hook
|
# effect相关hook
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> 面试题:说一说 useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect 的区别?
|
> 面试题:说一说 useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect 的区别?
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在 React 中,用于定义有副作用的因变量的 hook 有三个:
|
在 React 中,用于定义有副作用的因变量的 hook 有三个:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- useEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段完成后异步执行,所以它不会阻塞视图渲染
|
- useEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段完成后异步执行,所以它不会阻塞视图渲染
|
||||||
- useLayoutEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段的 Layout 子阶段同步执行,一般用于执行 DOM 相关的操作
|
- useLayoutEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段的 Layout 子阶段同步执行,一般用于执行 DOM 相关的操作
|
||||||
- useInsertionEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段的 Mutation 子阶段同步执行,与 useLayoutEffect 的区别在于执行的时候无法访问对 DOM 的引用。这个 Hook 是专门为 CSS-in-JS 库插入全局的 style 元素而设计。
|
- useInsertionEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段的 Mutation 子阶段同步执行,与 useLayoutEffect 的区别在于执行的时候无法访问对 DOM 的引用。这个 Hook 是专门为 CSS-in-JS 库插入全局的 style 元素而设计。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 数据结构
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 数据结构
|
对于这三个 effect 相关的 hook,hook.memoizedState 共同使用同一套数据结构:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
对于这三个 effect 相关的 hook,hook.memoizedState 共同使用同一套数据结构:
|
```js
|
||||||
|
const effect = {
|
||||||
```js
|
// 用于区分 effect 类型 Passive | Layout | Insertion
|
||||||
const effect = {
|
tag,
|
||||||
// 用于区分 effect 类型 Passive | Layout | Insertion
|
// effect 回调函数
|
||||||
tag,
|
create,
|
||||||
// effect 回调函数
|
// effect 销毁函数
|
||||||
create,
|
destory,
|
||||||
// effect 销毁函数
|
// 依赖项
|
||||||
destory,
|
deps,
|
||||||
// 依赖项
|
// 与当前 FC 的其他 effect 形成环状链表
|
||||||
deps,
|
next: null
|
||||||
// 与当前 FC 的其他 effect 形成环状链表
|
}
|
||||||
next: null
|
```
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
tag 用来区分 effect 的类型:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
tag 用来区分 effect 的类型:
|
- Passive: useEffect
|
||||||
|
- Layout:useLayoutEffect
|
||||||
- Passive: useEffect
|
- Insertion:useInsertionEffect
|
||||||
- Layout:useLayoutEffect
|
|
||||||
- Insertion:useInsertionEffect
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
create 和 destory 分别指代 effect 的回调函数以及 effect 销毁函数:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
create 和 destory 分别指代 effect 的回调函数以及 effect 销毁函数:
|
```js
|
||||||
|
useEffect(()=>{
|
||||||
```js
|
// create
|
||||||
useEffect(()=>{
|
return ()=>{
|
||||||
// create
|
// destory
|
||||||
return ()=>{
|
}
|
||||||
// destory
|
})
|
||||||
}
|
```
|
||||||
})
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
next 字段会与当前的函数组件的其他 effect 形成环状链表,连接的方式是一个单向环状链表。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
next 字段会与当前的函数组件的其他 effect 形成环状链表,连接的方式是一个单向环状链表。
|
```jsx
|
||||||
|
function App(){
|
||||||
```jsx
|
useEffect(()=>{
|
||||||
function App(){
|
console.log(1);
|
||||||
useEffect(()=>{
|
});
|
||||||
console.log(1);
|
const [num1, setNum1] = useState(0);
|
||||||
});
|
const [num2, setNum2] = useState(0);
|
||||||
const [num1, setNum1] = useState(0);
|
useEffect(()=>{
|
||||||
const [num2, setNum2] = useState(0);
|
console.log(2);
|
||||||
useEffect(()=>{
|
});
|
||||||
console.log(2);
|
useEffect(()=>{
|
||||||
});
|
console.log(3);
|
||||||
useEffect(()=>{
|
});
|
||||||
console.log(3);
|
|
||||||
});
|
return <div>Hello</div>
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
return <div>Hello</div>
|
```
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
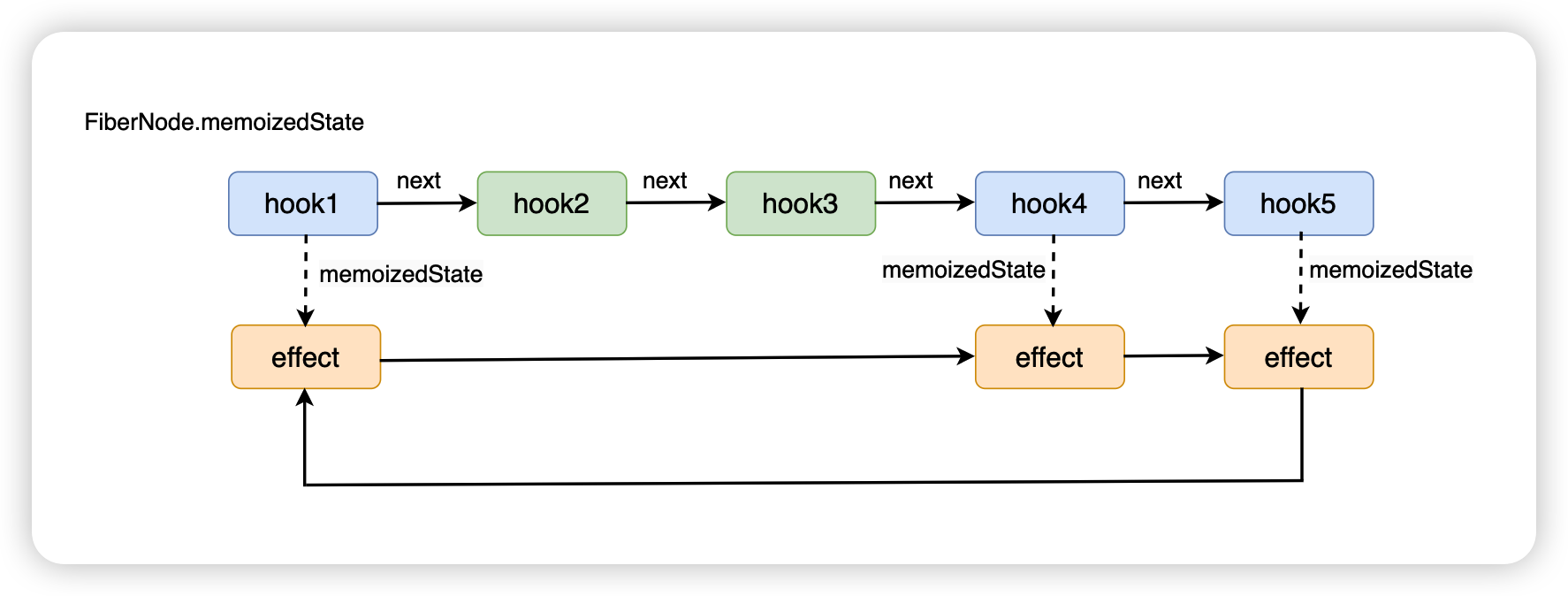
结构如下图所示:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
结构如下图所示:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
## 工作流程
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
整个工作流程可以分为三个阶段:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 工作流程
|
- 声明阶段
|
||||||
|
- 调度阶段(useEffect 独有的)
|
||||||
整个工作流程可以分为三个阶段:
|
- 执行阶段
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 声明阶段
|
|
||||||
- 调度阶段(useEffect 独有的)
|
|
||||||
- 执行阶段
|
### 声明阶段
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
声明阶段又可以分为 mount 和 update。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 声明阶段
|
mount 的时候执行的是 mountEffectImpl,相关代码如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
声明阶段又可以分为 mount 和 update。
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function mountEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps) {
|
||||||
mount 的时候执行的是 mountEffectImpl,相关代码如下:
|
// 生成 hook 对象
|
||||||
|
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
|
||||||
```js
|
// 保存依赖的数组
|
||||||
function mountEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps) {
|
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
|
||||||
// 生成 hook 对象
|
// 修改当前 fiber 的 flag
|
||||||
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
|
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
|
||||||
// 保存依赖的数组
|
// 将 pushEffect 返回的环形链表存储到 hook 对象的 memoizedState 中
|
||||||
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
|
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
|
||||||
// 修改当前 fiber 的 flag
|
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
|
||||||
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
|
create,
|
||||||
// 将 pushEffect 返回的环形链表存储到 hook 对象的 memoizedState 中
|
undefined,
|
||||||
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
|
nextDeps
|
||||||
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
|
);
|
||||||
create,
|
}
|
||||||
undefined,
|
```
|
||||||
nextDeps
|
|
||||||
);
|
在上面的代码中,首先生成 hook 对象,拿到依赖,修改 fiber 的 flag,之后将当前的 effect 推入到环状列表,hook.memoizedState 指向该环状列表。
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在上面的代码中,首先生成 hook 对象,拿到依赖,修改 fiber 的 flag,之后将当前的 effect 推入到环状列表,hook.memoizedState 指向该环状列表。
|
update 的时候执行的是 updateEffectImpl,相关代码如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function updateEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps) {
|
||||||
update 的时候执行的是 updateEffectImpl,相关代码如下:
|
// 先拿到之前的 hook 对象
|
||||||
|
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
|
||||||
```js
|
// 拿到依赖项
|
||||||
function updateEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps) {
|
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
|
||||||
// 先拿到之前的 hook 对象
|
|
||||||
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
|
// 初始化清除 effect 函数
|
||||||
// 拿到依赖项
|
let destroy = undefined;
|
||||||
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
|
|
||||||
|
if (currentHook !== null) {
|
||||||
// 初始化清除 effect 函数
|
// 从 hook 对象上面的 memoizedState 上面拿到副作用的环形链表
|
||||||
let destroy = undefined;
|
const prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState;
|
||||||
|
// 拿到销毁函数,也就是说副作用函数执行后返回的函数
|
||||||
if (currentHook !== null) {
|
destroy = prevEffect.destroy;
|
||||||
// 从 hook 对象上面的 memoizedState 上面拿到副作用的环形链表
|
// 如果新的依赖项不为空
|
||||||
const prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState;
|
if (nextDeps !== null) {
|
||||||
// 拿到销毁函数,也就是说副作用函数执行后返回的函数
|
const prevDeps = prevEffect.deps;
|
||||||
destroy = prevEffect.destroy;
|
// 两个依赖项进行比较
|
||||||
// 如果新的依赖项不为空
|
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
|
||||||
if (nextDeps !== null) {
|
// 如果依赖的值相同,即依赖没有变化,那么只会给这个 effect 打上一个 HookPassive 一个 tag
|
||||||
const prevDeps = prevEffect.deps;
|
// 然后在组件渲染完以后会跳过这个 effect 的执行
|
||||||
// 两个依赖项进行比较
|
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
|
||||||
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
|
return;
|
||||||
// 如果依赖的值相同,即依赖没有变化,那么只会给这个 effect 打上一个 HookPassive 一个 tag
|
}
|
||||||
// 然后在组件渲染完以后会跳过这个 effect 的执行
|
}
|
||||||
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
|
}
|
||||||
return;
|
// 如果deps依赖项发生改变,赋予 effectTag ,在commit节点,就会再次执行我们的effect
|
||||||
}
|
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
// pushEffect 的作用是将当前 effect 添加到 FiberNode 的 updateQueue 中,然后返回这个当前 effcet
|
||||||
// 如果deps依赖项发生改变,赋予 effectTag ,在commit节点,就会再次执行我们的effect
|
// 然后是把返回的当前 effect 保存到 Hook 节点的 memoizedState 属性中
|
||||||
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
|
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
|
||||||
|
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
|
||||||
// pushEffect 的作用是将当前 effect 添加到 FiberNode 的 updateQueue 中,然后返回这个当前 effcet
|
create,
|
||||||
// 然后是把返回的当前 effect 保存到 Hook 节点的 memoizedState 属性中
|
destroy,
|
||||||
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
|
nextDeps
|
||||||
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
|
);
|
||||||
create,
|
}
|
||||||
destroy,
|
```
|
||||||
nextDeps
|
|
||||||
);
|
在上面的代码中,首先从 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法中拿到 hook 对象,之后会从 hook.memoizedState 拿到所存储的 effect 对象,之后会利用 areHookInputsEqual 方法进行前后依赖项的比较,如果依赖相同,那就会在 effect 上面打一个 tag,在组件渲染完以后会跳过这个 effect 的执行。
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
如果依赖发生了变化,那么当前的 fiberNode 就会有一个 flags,回头在 commit 阶段统一执行该 effect,之后会推入新的 effect 到环状链表上面。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
在上面的代码中,首先从 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法中拿到 hook 对象,之后会从 hook.memoizedState 拿到所存储的 effect 对象,之后会利用 areHookInputsEqual 方法进行前后依赖项的比较,如果依赖相同,那就会在 effect 上面打一个 tag,在组件渲染完以后会跳过这个 effect 的执行。
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
如果依赖发生了变化,那么当前的 fiberNode 就会有一个 flags,回头在 commit 阶段统一执行该 effect,之后会推入新的 effect 到环状链表上面。
|
areHookInputsEqual 的作用是比较两个依赖项数组是否相同,采用的是浅比较,相关代码如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps){
|
||||||
areHookInputsEqual 的作用是比较两个依赖项数组是否相同,采用的是浅比较,相关代码如下:
|
// 省略代码
|
||||||
|
for(let i=0; i<prevDeps.length && i< nextDeps.length; i++){
|
||||||
```js
|
// 使用 Object.is 进行比较
|
||||||
function areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps){
|
if (is(nextDeps[i], prevDeps[i])) {
|
||||||
// 省略代码
|
continue;
|
||||||
for(let i=0; i<prevDeps.length && i< nextDeps.length; i++){
|
}
|
||||||
// 使用 Object.is 进行比较
|
return false;
|
||||||
if (is(nextDeps[i], prevDeps[i])) {
|
}
|
||||||
continue;
|
return true;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return false;
|
```
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return true;
|
pushEffect 方法的作用是生成一个 effect 对象,然后推入到当前的单向环状链表里面,相关代码如下:
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function pushEffect(tag, create, destroy, deps) {
|
||||||
pushEffect 方法的作用是生成一个 effect 对象,然后推入到当前的单向环状链表里面,相关代码如下:
|
// 创建副作用对象
|
||||||
|
const effect = {
|
||||||
```js
|
tag,
|
||||||
function pushEffect(tag, create, destroy, deps) {
|
create, // callback
|
||||||
// 创建副作用对象
|
destroy,
|
||||||
const effect = {
|
deps, // 依赖
|
||||||
tag,
|
// Circular
|
||||||
create, // callback
|
next: null,
|
||||||
destroy,
|
};
|
||||||
deps, // 依赖
|
|
||||||
// Circular
|
let componentUpdateQueue = currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue;
|
||||||
next: null,
|
|
||||||
};
|
// 创建单向环状链表
|
||||||
|
if (componentUpdateQueue === null) {
|
||||||
let componentUpdateQueue = currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue;
|
// 进入此 if,说明是第一个 effect
|
||||||
|
// createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue 调用后会返回一个对象
|
||||||
// 创建单向环状链表
|
// { lastEffect, events, stores, memoCache}
|
||||||
if (componentUpdateQueue === null) {
|
componentUpdateQueue = createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue();
|
||||||
// 进入此 if,说明是第一个 effect
|
// fiber 的 updateQueue 上面保存了该对象(componentUpdateQueue)
|
||||||
// createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue 调用后会返回一个对象
|
currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue = componentUpdateQueue;
|
||||||
// { lastEffect, events, stores, memoCache}
|
// 该对象(componentUpdateQueue)上面 lastEffect 存储了副作用对象
|
||||||
componentUpdateQueue = createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue();
|
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
|
||||||
// fiber 的 updateQueue 上面保存了该对象(componentUpdateQueue)
|
} else {
|
||||||
currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue = componentUpdateQueue;
|
// 存在多个 effect
|
||||||
// 该对象(componentUpdateQueue)上面 lastEffect 存储了副作用对象
|
// 拿到之前的副作用
|
||||||
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
|
const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect;
|
||||||
} else {
|
if (lastEffect === null) {
|
||||||
// 存在多个 effect
|
// 如果没有,那就和上面的 if 处理一样
|
||||||
// 拿到之前的副作用
|
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
|
||||||
const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect;
|
} else {
|
||||||
if (lastEffect === null) {
|
// 如果之前有副作用,先存储到 firstEffect
|
||||||
// 如果没有,那就和上面的 if 处理一样
|
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
|
||||||
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
|
// lastEffect 指向新的副作用对象
|
||||||
} else {
|
lastEffect.next = effect;
|
||||||
// 如果之前有副作用,先存储到 firstEffect
|
// 新的副作用对象的 next 指向之前的副作用对象
|
||||||
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
|
// 最终形成一个环形链表
|
||||||
// lastEffect 指向新的副作用对象
|
effect.next = firstEffect;
|
||||||
lastEffect.next = effect;
|
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect;
|
||||||
// 新的副作用对象的 next 指向之前的副作用对象
|
}
|
||||||
// 最终形成一个环形链表
|
}
|
||||||
effect.next = firstEffect;
|
return effect;
|
||||||
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect;
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
```
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return effect;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
update 的时候,即使 effect deps 没有变化,也会创建对应的 effect。因为这样才能后保证 effect 数量以及顺序是稳定的:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```js
|
||||||
|
// update 时 deps 没有变化情况
|
||||||
update 的时候,即使 effect deps 没有变化,也会创建对应的 effect。因为这样才能后保证 effect 数量以及顺序是稳定的:
|
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
|
||||||
|
// update 时 deps 有变化的情况
|
||||||
```js
|
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
|
||||||
// update 时 deps 没有变化情况
|
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
|
||||||
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
|
create,
|
||||||
// update 时 deps 有变化的情况
|
destroy,
|
||||||
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
|
nextDeps
|
||||||
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
|
);
|
||||||
create,
|
```
|
||||||
destroy,
|
|
||||||
nextDeps
|
|
||||||
);
|
|
||||||
```
|
### 调度阶段(useEffect 独有的)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
调度阶段是 useEffect 独有的,因为 useEffect 的回调函数会在 commit 阶段完成后异步执行,因此需要调度阶段。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 调度阶段(useEffect 独有的)
|
在 commit 阶段的三个子阶段开始之前,会执行如下的代码:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
调度阶段是 useEffect 独有的,因为 useEffect 的回调函数会在 commit 阶段完成后异步执行,因此需要调度阶段。
|
```js
|
||||||
|
if (
|
||||||
在 commit 阶段的三个子阶段开始之前,会执行如下的代码:
|
(finishedWork.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags ||
|
||||||
|
(finishedWork.flags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags
|
||||||
```js
|
) {
|
||||||
if (
|
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
|
||||||
(finishedWork.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags ||
|
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
|
||||||
(finishedWork.flags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags
|
pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes = remainingLanes;
|
||||||
) {
|
// ...
|
||||||
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
|
// scheduleCallback 来自于 Scheduler,用于以某一优先级调度回调函数
|
||||||
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
|
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
|
||||||
pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes = remainingLanes;
|
// 执行 effect 回调函数的具体方法
|
||||||
// ...
|
flushPassiveEffects();
|
||||||
// scheduleCallback 来自于 Scheduler,用于以某一优先级调度回调函数
|
return null;
|
||||||
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
|
});
|
||||||
// 执行 effect 回调函数的具体方法
|
}
|
||||||
flushPassiveEffects();
|
}
|
||||||
return null;
|
```
|
||||||
});
|
|
||||||
}
|
flushPassiveEffects 会去执行对应的 effects:
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function flushPassiveEffects(){
|
||||||
flushPassiveEffects 会去执行对应的 effects:
|
if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null) {
|
||||||
|
// 执行 effects
|
||||||
```js
|
}
|
||||||
function flushPassiveEffects(){
|
return false;
|
||||||
if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null) {
|
}
|
||||||
// 执行 effects
|
```
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return false;
|
另外,由于调度阶段的存在,为了保证下一次的 commit 阶段执行前,上一次 commit 所调度的 useEffect 都已经执行过了,因此会在 commit 阶段的入口处,也会执行 flushPassiveEffects,而且是一个循环执行:
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function commitRootImpl(root, renderPriorityLevel){
|
||||||
另外,由于调度阶段的存在,为了保证下一次的 commit 阶段执行前,上一次 commit 所调度的 useEffect 都已经执行过了,因此会在 commit 阶段的入口处,也会执行 flushPassiveEffects,而且是一个循环执行:
|
do {
|
||||||
|
flushPassiveEffects();
|
||||||
```js
|
} while (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null);
|
||||||
function commitRootImpl(root, renderPriorityLevel){
|
}
|
||||||
do {
|
```
|
||||||
flushPassiveEffects();
|
|
||||||
} while (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null);
|
之所以使用 do...while 循环,就是为了保证上一轮调度的 effect 都执行过了。
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
之所以使用 do...while 循环,就是为了保证上一轮调度的 effect 都执行过了。
|
### 执行阶段
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
这三个 effect 相关的 hook 执行阶段,有两个相关的方法
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### 执行阶段
|
- commitHookEffectListUnmount :用于遍历 effect 链表依次执行 effect.destory 方法
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
这三个 effect 相关的 hook 执行阶段,有两个相关的方法
|
```js
|
||||||
|
function commitHookEffectListUnmount(
|
||||||
- commitHookEffectListUnmount :用于遍历 effect 链表依次执行 effect.destory 方法
|
flags: HookFlags,
|
||||||
|
finishedWork: Fiber,
|
||||||
```js
|
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
|
||||||
function commitHookEffectListUnmount(
|
) {
|
||||||
flags: HookFlags,
|
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
|
||||||
finishedWork: Fiber,
|
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
|
||||||
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
|
if (lastEffect !== null) {
|
||||||
) {
|
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
|
||||||
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
|
let effect = firstEffect;
|
||||||
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
|
do {
|
||||||
if (lastEffect !== null) {
|
if ((effect.tag & flags) === flags) {
|
||||||
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
|
// Unmount
|
||||||
let effect = firstEffect;
|
// 从 effect 对象上面拿到 destory 函数
|
||||||
do {
|
const destroy = effect.destroy;
|
||||||
if ((effect.tag & flags) === flags) {
|
effect.destroy = undefined;
|
||||||
// Unmount
|
// ...
|
||||||
// 从 effect 对象上面拿到 destory 函数
|
}
|
||||||
const destroy = effect.destroy;
|
effect = effect.next;
|
||||||
effect.destroy = undefined;
|
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
|
||||||
// ...
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
effect = effect.next;
|
```
|
||||||
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
|
|
||||||
}
|
- commitHookEffectListMount:遍历 effect 链表依次执行 create 方法,在声明阶段中,update 时会根据 deps 是否变化打上不同的 tag,之后在执行阶段就会根据是否有 tag 来决定是否要执行该 effect
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```js
|
||||||
|
// 类型为 useInsertionEffect 并且存在 HasEffect tag 的 effect 会执行回调
|
||||||
- commitHookEffectListMount:遍历 effect 链表依次执行 create 方法,在声明阶段中,update 时会根据 deps 是否变化打上不同的 tag,之后在执行阶段就会根据是否有 tag 来决定是否要执行该 effect
|
commitHookEffectListMount(Insertion | HasEffect, fiber);
|
||||||
|
// 类型为 useEffect 并且存在 HasEffect tag 的 effect 会执行回调
|
||||||
```js
|
commitHookEffectListMount(Passive | HasEffect, fiber);
|
||||||
// 类型为 useInsertionEffect 并且存在 HasEffect tag 的 effect 会执行回调
|
// 类型为 useLayoutEffect 并且存在 HasEffect tag 的 effect 会执行回调
|
||||||
commitHookEffectListMount(Insertion | HasEffect, fiber);
|
commitHookEffectListMount(Layout | HasEffect, fiber);
|
||||||
// 类型为 useEffect 并且存在 HasEffect tag 的 effect 会执行回调
|
```
|
||||||
commitHookEffectListMount(Passive | HasEffect, fiber);
|
|
||||||
// 类型为 useLayoutEffect 并且存在 HasEffect tag 的 effect 会执行回调
|
|
||||||
commitHookEffectListMount(Layout | HasEffect, fiber);
|
|
||||||
```
|
由于 commitHookEffectListUnmount 方法的执行时机会先于 commitHookEffectListMount 方法执行,因此每次都是先执行 effect.destory 后才会执行 effect.create。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 真题解答
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
由于 commitHookEffectListUnmount 方法的执行时机会先于 commitHookEffectListMount 方法执行,因此每次都是先执行 effect.destory 后才会执行 effect.create。
|
> 题目:说一说 useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect 的区别?
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
|
> 参考答案:
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
## 真题解答
|
> 在 React 中,用于定义有副作用因变量的 Hook 有:
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
> 题目:说一说 useEffect 和 useLayoutEffect 的区别?
|
> - useEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段完成后异步执行,所以不会阻塞视图渲染
|
||||||
>
|
> - useLayoutEffect:回调函数会在 commit 阶段的 Layout 子阶段同步执行,一般用于执行 DOM 相关的操作
|
||||||
> 参考答案:
|
>
|
||||||
>
|
> 每一个 effect 会与当前 FC 其他的 effect 形成环状链表,连接方式为单向环状链表。
|
||||||
>
|
>
|
||||||
|
> 其中 useEffect 工作流程可以分为:
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
|
> - 声明阶段
|
||||||
|
> - 调度阶段
|
||||||
|
> - 执行阶段
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
|
> useLayoutEffect 的工作流程可以分为:
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
|
> - 声明阶段
|
||||||
|
> - 执行阶段
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
|
> 之所以 useEffect 会比 useLayoutEffect 多一个阶段,就是因为 useEffect 的回调函数会在 commit 阶段完成后异步执行,因此需要经历调度阶段。
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user