新增就业篇课件
197
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课件资料/1. 属性默认值和类型验证.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,197 @@
|
||||
# 1. 属性默认值和类型验证
|
||||
|
||||
在 *Vue* 中,我们可以针对 *props* 属性进行类型验证,那么在 *React* 中同样也能对 *props* 进行验证。
|
||||
|
||||
>官网文档地址:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/typechecking-with-proptypes.html*
|
||||
|
||||
从 *React v15.5* 开始,*React.PropTypes* 已移入另一个包中。因此首先我们需要安装 *prop-types* 库。
|
||||
|
||||
>*prop-types* 库文档地址:*https://www.npmjs.com/package/prop-types*
|
||||
|
||||
有关 *props* 验证这一块,我们主要需要搞清楚以下几个知识点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 提供了哪些验证类型
|
||||
- 如何设置默认值
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证类型
|
||||
|
||||
有关 *props* 能够验证的类型,官网实际上已经全部罗列出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
>对应地址:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/typechecking-with-proptypes.html#proptypes*
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个简单示例。
|
||||
|
||||
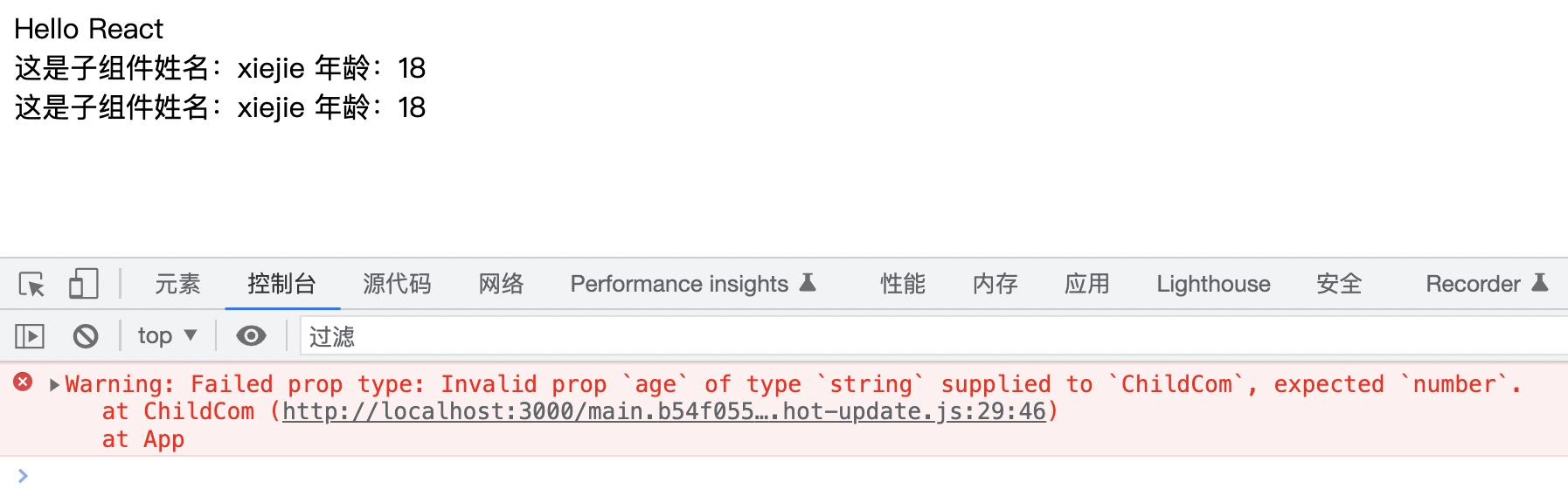
在根组件中我们使用到了子组件,并向子组件传递了 *name* 和 *age* 这两个 *props* 属性:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom from "./components/ChildCom"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className="App">
|
||||
Hello React
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie" age={18}/>
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie" age="18"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在子组件中,我们针对 *props* 做了类型的限制,要求 *name* 为 *string* 类型,*age* 为 *number* 类型:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
这是子组件
|
||||
<span>姓名:{props.name} 年龄:{props.age}</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ChildCom.propTypes = {
|
||||
name: PropTypes.string,
|
||||
age : PropTypes.number,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
浏览器效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果官方为你提供的验证规则不够用?没关系,我们还可以自定义验证器,它在验证失败时应返回一个 *Error* 对象。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
ChildCom.propTypes = {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param {*} props 传入的整体 props 对象
|
||||
* @param {*} propName 当前所验证的 props 属性
|
||||
* @param {*} componentName 组件名
|
||||
*/
|
||||
name: function (props, propName, componentName) {
|
||||
if (!/-stu/.test(props[propName])) {
|
||||
return new Error(
|
||||
'Invalid prop `' + propName + '` supplied to' +
|
||||
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
age: PropTypes.number,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们为 *name* 这个 *props* 属性自定义了验证器,要求传入的属性值必须包含 *-stu* 字符,因此在使用子组件时,下面的用法无法通过验证
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie" age={18}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 *name* 对应的值中需要包含 *-stu* 字符,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie-stu" age={18}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
另外,针对 *props* 是数组或者对象时,如果要验证的不仅仅是否是数组或对象类型,而是要验证数组和对象的每一项,那么可以使用 arrayOf 或 objectOf 验证器。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,我们现在有一个需求,要求数组的每一项为数字,验证器示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {*} propValue props 对象的数组或对象值
|
||||
* @param {*} key 数组或者对象的 key
|
||||
* @param {*} componentName 组件名
|
||||
* @param {*} location 位置
|
||||
* @param {*} propFullName arr[index] or object.xx
|
||||
*/
|
||||
score: PropTypes.arrayOf(function (propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName) {
|
||||
console.log(propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName);
|
||||
if (typeof propValue[key] !== 'number') {
|
||||
return new Error(
|
||||
'Invalid prop `' + propFullName + '` supplied to' +
|
||||
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
子组件下面的 *props* 是无法通过验证的:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie-stu" age={18} score={[98,"97",100]}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*score* 对应的数组值每一项都应该为 *number* 类型,以下的用法能够通过验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie-stu" age={18} score={[98, 97, 100]} />
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 插槽的验证
|
||||
|
||||
之前在入门篇我们介绍过 *React* 的插槽也是使用 *props* 来实现的。
|
||||
|
||||
针对插槽,使用 *prop-types* 可以进行插槽元素的单一验证,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
下面是插槽显示的内容
|
||||
{props.children}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ChildCom.propTypes = {
|
||||
children: PropTypes.element.isRequired
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的示例中,我们为 *ChildCom* 设置了一个插槽,并且设置了一个验证,要求父组件在使用 *ChildCom* 子组件时,必须要插入一个根元素。
|
||||
|
||||
以下的使用方式无法通过验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom />
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom>
|
||||
<div>Hello</div>
|
||||
<div>World</div>
|
||||
</ChildCom>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以下的方式可以通过验证:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom>
|
||||
<div>Hello</div>
|
||||
</ChildCom>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 默认值
|
||||
|
||||
*props* 属性还可以设置默认值,这一点官网已经有了很好的示例,请参阅:
|
||||
|
||||
>*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/typechecking-with-proptypes.html#default-prop-values*
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
17
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
17
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
import ChildCom from "./components/ChildCom"
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<ChildCom name="xiejie-stu" age={18} score={[98, 97, 100]}>
|
||||
<div>hello</div>
|
||||
</ChildCom>
|
||||
|
||||
<ChildCom age={18} score={[98, 97, 100]}>
|
||||
<div>world</div>
|
||||
</ChildCom>
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
这是子组件
|
||||
<span>姓名:{props.name} 年龄:{props.age}</span>
|
||||
<div>{props.children}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 书写关于 props 类型的验证
|
||||
ChildCom.propTypes = {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param {*} props 整体的 props 对象 {name:... , age :...}
|
||||
* @param {*} propName 当前验证的 props 属性 name
|
||||
* @param {*} componentName 组件名
|
||||
*/
|
||||
name: function (props, propName, componentName) {
|
||||
if (!/-stu/.test(props[propName])) {
|
||||
// 进入此 if, 说明验证没有通过
|
||||
return new Error(
|
||||
'Invalid prop `' + propName + '` supplied to' +
|
||||
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
age: PropTypes.number,
|
||||
score: PropTypes.arrayOf(function (propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName) {
|
||||
if (typeof propValue[key] !== 'number') {
|
||||
return new Error(
|
||||
'Invalid prop `' + propFullName + '` supplied to' +
|
||||
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}),
|
||||
children: PropTypes.element.isRequired
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 书写默认值
|
||||
ChildCom.defaultProps = {
|
||||
name : 'jiexie-stu'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom;
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-1. 属性默认值和类型验证/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
236
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课件资料/2. 高阶组件.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
# 2. 高阶组件
|
||||
|
||||
高阶组件英语全称为 *Higher-Order Components*,简称 *HOC*,所谓高阶组件,是 *React* 中一种复用逻辑的技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
高阶组件的学习,主要有下面 *2* 个点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 认识到高阶组件并非一个组件,而是增强组件功能的一个函数
|
||||
- 高阶组件的作用是对多组件公共逻辑进行**横向**抽离
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 高阶组件是一个函数
|
||||
|
||||
这个点非常有意思,很多人一看到这个名字,自然的会认为高阶组件是一个组件,但是往往有些名字具有欺骗性,就像 *JavaScript* 会被误认为和 *Java* 相关一样。
|
||||
|
||||
官方对高阶组件给出了很明确的定义,甚至还给了一个公式:
|
||||
|
||||
>**高阶组件是参数为组件,返回值为新组件的函数。**
|
||||
>
|
||||
>```js
|
||||
>const EnhancedComponent = higherOrderComponent(WrappedComponent);
|
||||
>```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 高阶组件要做的事情
|
||||
|
||||
高阶组件作为一个函数,接收你传入的组件,然后又返回一个新组件给你,那你猜都猜得到在高阶组件的内部肯定是对你原有的组件做了一些增强操作,然后为你返回的是增强后的组件。
|
||||
|
||||
那什么又叫做对组件**公共逻辑**进行**横向抽离**呢?看下图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
假设我们这里有三个组件,每个组件有一部分**公共逻辑**,一部分该组件自身的**业务逻辑**,那么很明显每个组件都书写一遍这样的公共逻辑是不划算的。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个程序员,我们自然而然想到的就是将这部分公共逻辑提取出来。
|
||||
|
||||
早期的 *React* 采用的是 *mixins* 来解决这种横切关注点相关的问题。*Mixins* 的原理可以简单理解为将一个 *mixin* 对象上的方法增加到组件上。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const mixinDefaultProps = {}
|
||||
const ExampleComponent = React.createClasss({
|
||||
mixins: [mixinDefaultProps],
|
||||
render: function(){}
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
眼熟不?没错,在 *Vue2.x* 中也支持 *mixins* 这样的混合注入。
|
||||
|
||||
不过这只能在 *React* 的旧语法 *React.createClasss* 中使用,目前已经不再推荐使用了。
|
||||
|
||||
>*mixins 问题*
|
||||
>
|
||||
>- *mixins* 引入了隐式的依赖关系
|
||||
>
|
||||
>你可能会写一个有状态的组件,然后你的同事可能添加一个读取这个组件 *state* 的 *mixin*。几个月之后,你可能希望将该 *state* 移动到父组件,以便与其兄弟组件共享。你会记得更新这个 *mixin* 来读取 *props* 而不是 *state* 吗?如果此时,其它组件也在使用这个 *mixin* 呢?
|
||||
>
|
||||
>- *mixins* 引起名称冲突
|
||||
>
|
||||
>无法保证两个特定的 *mixin* 可以一起使用。例如,如果 *FluxListenerMixin* 和 *WindowSizeMixin* 都定义来 *handleChange( )*,则不能一起使用它们。同时,你也无法在自己的组件上定义具有此名称的方法。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>- *mixins* 导致滚雪球式的复杂性
|
||||
>
|
||||
>每一个新的需求都使 *mixins* 更难理解。使用相同 *mixin* 的组件会随着时间的推移变得越来越耦合。任何新功能都可以使用 *mixins* 添加到所有组件中。渐渐地,封装边界被侵蚀了,由于很难更改或删除现有的 *mixins*,它们变得越来越抽象,直到没有人理解它们是如何工作的。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>关于 *mixin* 的讨论,可以参阅官方文档:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/blog/2016/07/13/mixins-considered-harmful.html*
|
||||
|
||||
之后 *React* 推出了高阶组件的抽离方式,如下图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-054950.png" alt="image-20221130134950363" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
在高阶组件中,接收一个组件作为参数,然后在高阶组件中会返回一个新组件,新组件中会将公共逻辑附加上去,传入的组件一般作为新组件的视图。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个具体的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
子组件1
|
||||
姓名:{props.name}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom2(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
子组件2
|
||||
年龄:{props.age}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的代码中,我们有两个子组件,父组件在使用这两个子组件时,一个需要传入 *name*,另一个需要传入 *age*
|
||||
|
||||
正常来讲,父组件使用子组件的方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<ChildCom1 name="xiejie"/>
|
||||
<ChildCom2 age={18}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但是现在我们新增了一个需求,那就是每个子组件需要记录创建和销毁时的日志。很显然,对于每个子组件来讲,日志相关的逻辑都是相同的,也就算是公共逻辑,没有必要在每个组件中引入一份,因此这里我们来使用 *HOC* 的方式抽离这一段公共逻辑,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useEffect } from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools"
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withLog(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
return function NewCom(props) {
|
||||
// 抽离的公共逻辑
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
console.log(`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(Date.now(),"year-time")}`);
|
||||
return function(){
|
||||
console.log(`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(Date.now(),"year-time")}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
},[]);
|
||||
// 一般来讲,传入的组件会作为新组件的视图
|
||||
return <Com {...props}/>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withLog;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的高阶组件中,唯一需要注意的就是返回的新组件在接受了 *props* 后,一般需要原封不动的传递给原来的组件。
|
||||
|
||||
有了这个高阶组件后,我们就可以对原有的子组件进行加强,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
import withLog from "./HOC/withLog"
|
||||
import { useState } from "react"
|
||||
|
||||
// 对原有的子组件进行加强操作
|
||||
const WrapChild1 = withLog(ChildCom1);
|
||||
const WrapChild2 = withLog(ChildCom2);
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
const [toggle, setToggle] = useState(true);
|
||||
const child = toggle ? <WrapChild1 name="xiejie" /> : <WrapChild2 age={18} />;
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{/* 按钮对两个组件进行切换,查看日志功能 */}
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setToggle(!toggle)}>show/hide</button>
|
||||
{child}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
实际效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
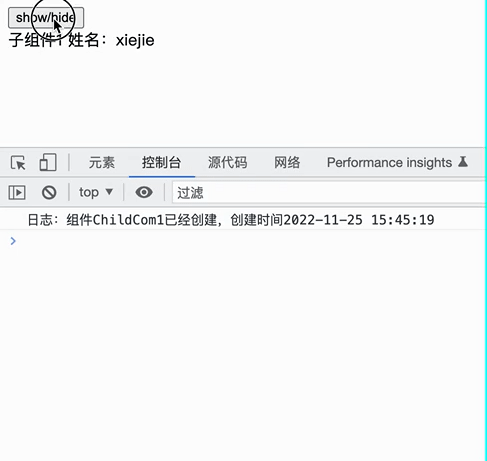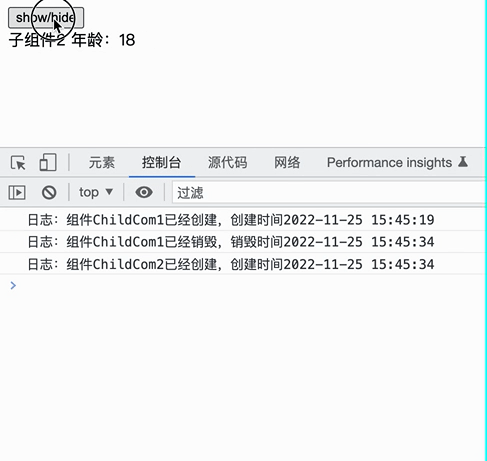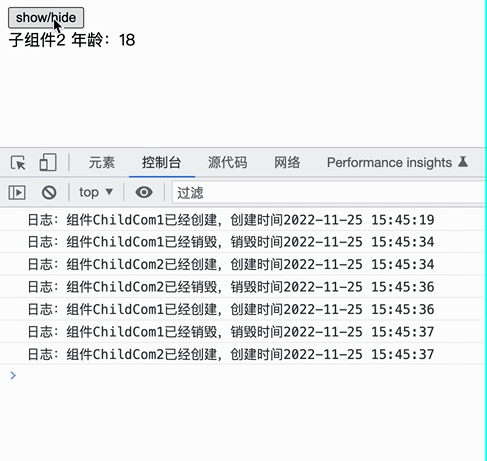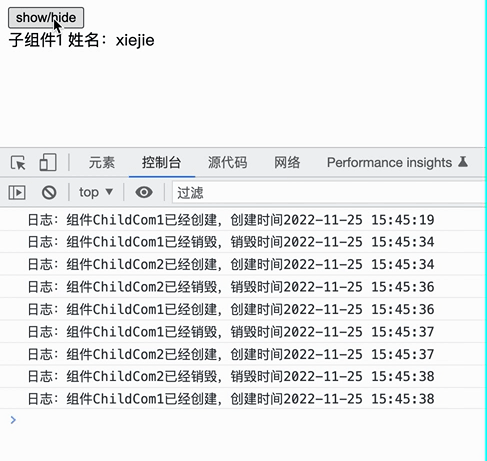
|
||||
|
||||
高阶组件还可以进行嵌套操作,比如我有两段公共逻辑,但是这两段公共逻辑写在一个高阶组件中又不太合适,因此我们就可以拆分成两个高阶组件,例如我们新增一个 *withTimer* 的高阶组件:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withTimer(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
return function NewCom(props) {
|
||||
// 抽离的公共逻辑
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
const stopTimer = setInterval(() => {
|
||||
console.log(counter);
|
||||
setCounter(counter + 1);
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
return function () {
|
||||
clearInterval(stopTimer);
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 一般来讲,传入的组件会作为新组件的视图
|
||||
return <Com {...props} />;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withTimer;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后在使用高阶组件时,就可以采取嵌套的方式来使用:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const WrapChild1 = withTimer(withLog(ChildCom1));
|
||||
const WrapChild2 = withTimer(withLog(ChildCom2));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 高阶组件的现状
|
||||
|
||||
高阶组件的出现,解决了组件之间如何横向抽离公共逻辑的问题,因此你也能过在各大生态库中见到高阶组件的身影。
|
||||
|
||||
例如在 *react-redux* 中的 *connect* 用法,这里 *connect* 明显返回的就是一个高阶组件,之后开发者可以传入自己的组件进行组件强化。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
connect()(MyComponent)
|
||||
connect(mapState)(MyComponent)
|
||||
connect(mapState, null, mergeProps, options)(MyComponent)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>*https://react-redux.js.org/api/connect#connect-returns*
|
||||
|
||||
不过有意思的是,如果你查阅官网,会发现官网给的示例基本都是类组件的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
>*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/higher-order-components.html*
|
||||
|
||||
没错,*HOC* 实际上就是为了解决早期**类组件**的公共逻辑抽离的问题,那个时候在 *React* 中类组件占主流。但是随着目前 *Hook* 的出现,函数组件开始占主流,*React* 开发的思想也从面向对象转为了函数式编程,抽离公共逻辑也能够非常简单的使用自定义 *Hook* 来实现了。
|
||||
|
||||
因此你在 *react-redux* 官网也能看到这样一句话:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055117.png" alt="image-20221130135117223" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
17
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
22
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
import withLog from "./HOC/withLog";
|
||||
import withTimer from "./HOC/withTimer";
|
||||
import { useState } from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
const NewChildCom1 = withTimer(withLog(ChildCom1));
|
||||
const NewChildCom2 = withTimer(withLog(ChildCom2));
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [toggle, setToggle] = useState(true);
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onClick={()=>setToggle(!toggle)}>切换</button>
|
||||
{toggle ? <NewChildCom1 name="谢杰"/> : <NewChildCom2 age={18}/>}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
21
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/src/HOC/withLog.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
import {useEffect} from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools";
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 在接收的组件上面添加一些公共的逻辑
|
||||
* @param {*} Com 接收一个组件
|
||||
* @returns 返回一个新组件
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function withLog(Com){
|
||||
return function NewCom(props){
|
||||
// 抽离的公共逻辑
|
||||
useEffect(()=>{
|
||||
console.log(`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(Date.now(),"year-time")}`);
|
||||
return function(){
|
||||
console.log(`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(Date.now(),"year-time")}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
},[])
|
||||
// 一般来讲,传入的组件会作为新组件的视图
|
||||
return <Com {...props} />
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
26
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/src/HOC/withTimer.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 为组件添加 timer
|
||||
* @param {*} Com 旧组件
|
||||
* @returns 新的组件
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function withTimer(Com){
|
||||
return function NewCom(props){
|
||||
// 抽离公共逻辑
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(()=>{
|
||||
const stopTimer = setInterval(()=>{
|
||||
console.log(counter);
|
||||
setCounter(counter + 1);
|
||||
},1000);
|
||||
|
||||
return function(){
|
||||
clearInterval(stopTimer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
},[counter]);
|
||||
|
||||
return <Com {...props}/>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
这是子组件1
|
||||
<div>姓名:{props.name}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
function ChildCom2(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
这是子组件2
|
||||
<div>年龄:{props.age}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
80
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-2. 高阶组件/课堂代码/my-app/src/utils/tools.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 格式化时间戳
|
||||
* @param {*} timestamp
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export function formatDate(timestamp, part) {
|
||||
if (!timestamp) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let date = new Date(parseInt(timestamp));
|
||||
|
||||
let year = date.getFullYear(); // 年
|
||||
let month = date.getMonth() + 1; // 月
|
||||
let day = date.getDate(); // 日
|
||||
|
||||
let hour = date.getHours(); // 时
|
||||
let minutes = date.getMinutes(); // 分
|
||||
let seconds = date.getSeconds(); // 秒
|
||||
|
||||
let weekArr = [
|
||||
"星期日",
|
||||
"星期一",
|
||||
"星期二",
|
||||
"星期三",
|
||||
"星期四",
|
||||
"星期五",
|
||||
"星期六",
|
||||
];
|
||||
let week = weekArr[date.getDay()];
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要给一位数前面加 0
|
||||
// 9 点 ----> 09:45:03
|
||||
|
||||
if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) {
|
||||
// month += '0'; // a += b ----> a = a + b
|
||||
month = "0" + month;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (day >= 0 && day <= 9) {
|
||||
day = "0" + day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (hour >= 0 && hour <= 9) {
|
||||
hour = "0" + hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minutes >= 0 && minutes <= 9) {
|
||||
minutes = "0" + minutes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (seconds >= 0 && seconds <= 9) {
|
||||
seconds = "0" + seconds;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var str = "";
|
||||
|
||||
switch (part) {
|
||||
case "year": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} `;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "year-time": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time-week": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
567
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课件资料/3. Ref.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,567 @@
|
||||
# 3. *Ref*
|
||||
|
||||
关于 *Ref*,我们在前面入门篇实际上已经有所涉及了,当时通过 *Ref* 获取到 *markdown* 编辑器的 *DOM* 节点,然后获取用户所输入的文档内容。
|
||||
|
||||
这一讲,我们就来彻底看一下 *Ref*,包含以下的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
- 过时 *API*:*String* 类型的 *Refs*
|
||||
- *createRef API*
|
||||
- *Ref* 转发
|
||||
- *useRef* 与 *useImperativeHandle*
|
||||
|
||||
## 过时 *API*:*String* 类型的 *Refs*
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们还是需要认识到 *Ref* 是为了解决什么问题。我们都知道,现代前端框架的一大特点就是响应式,开发人员不需要再去手动操作 *DOM* 元素,只需要关心和 *DOM* 元素绑定的响应式数据即可。
|
||||
|
||||
但是有些时候,我们需要操作 *DOM* 元素,例如官方所列举的这几个场景:
|
||||
|
||||
- 管理焦点,文本选择或媒体播放
|
||||
- 触发强制动画
|
||||
- 集成第三方 *DOM* 库
|
||||
|
||||
在最最早期的时候,*React* 中 *Ref* 的用法非常简单,类似于 *Vue*,给一个字符串类型的值,之后在方法中通过 *this.refs.xxx* 就能够引用到。
|
||||
|
||||
示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
clickHandle = () => {
|
||||
console.log(this);
|
||||
console.log(this.refs.inputRef);
|
||||
this.refs.inputRef.focus();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<input type="text" ref="inputRef"/>
|
||||
<button onClick={this.clickHandle}>聚焦</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们在 *input* 上面挂了一个 *ref* 属性,对应的值为 *inputRef*,之后查看组件实例,可以看到该组件实例中的 *refs* 里面就保存了该 *input* 的 *DOM* 元素。
|
||||
|
||||
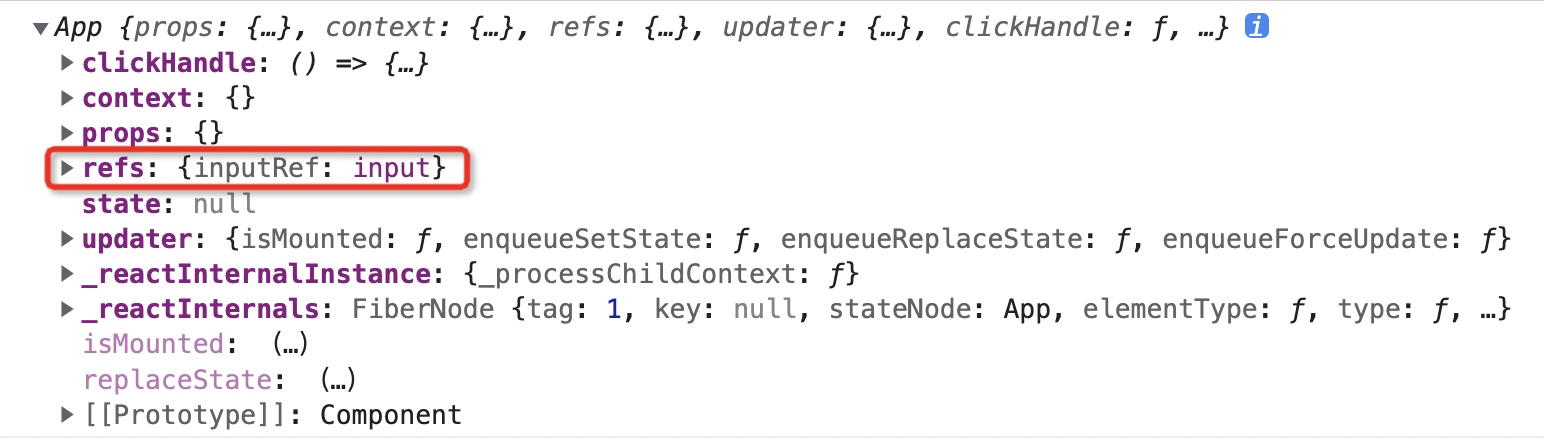
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们就可以像之前一样进行 *DOM* 元素的操作了。例如在上面的示例中我们进行了聚焦的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
但是这里需要注意两点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 避免使用 *refs* 来做任何可以通过声明式实现来完成的事情
|
||||
- 该 *API* 已经过时,可能会在未来的版本被移除,官方建议我们使用回调函数或 *createRef API* 的方式来代替
|
||||
|
||||
参阅官网 *https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/refs-and-the-dom.html#legacy-api-string-refs*
|
||||
|
||||
至于为什么 *String* 类型的 *Refs* 会被废弃,主要是以下几个方面原因:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
参阅地址:*https://github.com/facebook/react/pull/8333#issuecomment-271648615*
|
||||
|
||||
## *createRef API*
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们来看一下官方推荐的 *createRef API*。
|
||||
|
||||
示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.inputRef = React.createRef();
|
||||
console.log(this.inputRef); // {current: null}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
clickHandle = () => {
|
||||
console.log(this.inputRef); // {current: input}
|
||||
this.inputRef.current.focus();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<input type="text" ref={this.inputRef}/>
|
||||
<button onClick={this.clickHandle}>聚焦</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们创建 *Ref* 不再是通过字符串的形式,而是采用的 *createRef* 这个静态方法创建了一个 *Ref* 对象,并在组件实例上面新增了一个 *inputRef* 属性来保存这个 *Ref* 对象。
|
||||
|
||||
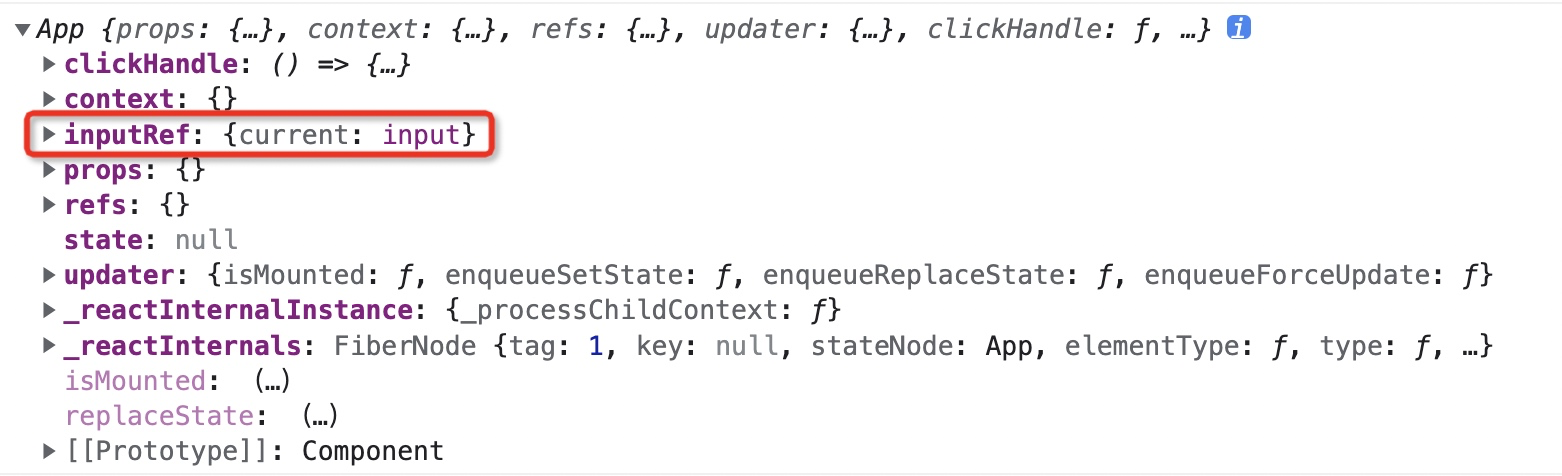
|
||||
|
||||
*createRef* 这个方法本质也很简单,就是返回了一个 *{current: null}* 的对象,下面是 *createRef* 的源码:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055424.png" alt="image-20221130135424421" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
最后我们把这个对象和 *input* 进行关联。
|
||||
|
||||
如果要获取 *DOM* 元素,可以通过 *this.inputRef.current* 来获取。
|
||||
|
||||
除了在 *JSX* 中关联 *Ref*,我们还可以直接关联一个类组件,这样就可以直接调用该组件内部的方法。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 子组件
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ChildCom1 extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
test = () => {
|
||||
console.log("这是子组件的 test 方法");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>ChildCom1</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 父组件
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.comRef = React.createRef();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
clickHandle = () => {
|
||||
console.log(this);
|
||||
console.log(this.comRef); // {current: ChildCom1}
|
||||
this.comRef.current.test();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{/* ref 关联子组件 */}
|
||||
<ChildCom1 ref={this.comRef}/>
|
||||
<button onClick={this.clickHandle}>触发子组件方法</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>虽然提供这种方式,但这是一种**反模式**,相当于回到了 *jQuery* 时代,因此尽量避免这么做。
|
||||
|
||||
*React.createRef API* 是在 *React 16.3* 版本引入的,如果是稍早一点的版本,官方推荐使用回调 *Refs*,也就是函数的形式。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.inputRef = element => {
|
||||
this.inputDOM = element;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.comRef = element => {
|
||||
this.comInstance = element;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
clickHandle = () => {
|
||||
this.inputDOM.focus();
|
||||
this.comInstance.test();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{/* ref 关联子组件 */}
|
||||
<input type="text" ref={this.inputRef} />
|
||||
<ChildCom1 ref={this.comRef} />
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onClick={this.clickHandle}>聚焦并且触发子组件方法</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会好奇,为什么上面的例子都是使用的类组件,现在不都是使用函数组件了么?这是因为默认情况下,你不能在**函数组件上**使用 *ref* 属性,因为它们没有实例,但是在函数组件内部是可以使用 *ref* 的,这涉及到后面要说的 *useRef*。
|
||||
|
||||
## *Ref* 转发
|
||||
|
||||
既然要讲 *Ref*,咱们就一起把它整个知识点一起讲完,接下来要介绍的是*Ref* 的转发。
|
||||
|
||||
*Ref* 转发是一个可选特性,其允许某些组件接收 *ref*,并将其向下传递(换句话说,“转发”它)给子组件。
|
||||
|
||||
那么什么时候需要 *Ref* 的转发呢?往往就在使用高阶组件的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
我们先来看一下如果没有 *Ref* 转发,在高阶组件中使用 *Ref* 会遇到什么问题。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// App.jsx
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
import withLogin from "./HOC/withLog";
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
const NewChild = withLogin(ChildCom1);
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.comRef = React.createRef();
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
show: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
clickHandle = () => {
|
||||
// 查看当前的 Ref 所关联的组件
|
||||
console.log(this.comRef);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => this.setState({
|
||||
show: !this.state.show
|
||||
})}>show/hide</button>
|
||||
<button onClick={this.clickHandle}>触发子组件方法</button>
|
||||
{this.state.show ? <NewChild ref={this.comRef} /> : null}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// withLog.js
|
||||
import { Component } from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools";
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withLog(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
return class extends Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = { n: 1 };
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentDidMount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentWillUnmount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return <Com {...this.props} />;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withLog;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// ChildCom1.jsx
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ChildCom1 extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
test = () => {
|
||||
console.log("这是子组件的 test 方法");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>ChildCom1</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的三段代码中,我们使用了 *withLog* 这个高阶组件来包裹 *ChildCom1* 子组件,从而添加日志功能。在使用由高阶组件返回的增强组件时,我们传递了一个 *Ref*,我们的本意是想要这个 *Ref* 关联原本的子组件,从而可以触发子组件里面的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我们会发现 *Ref* 关联的是高阶组件中返回增强组件,而非原来的子组件。
|
||||
|
||||
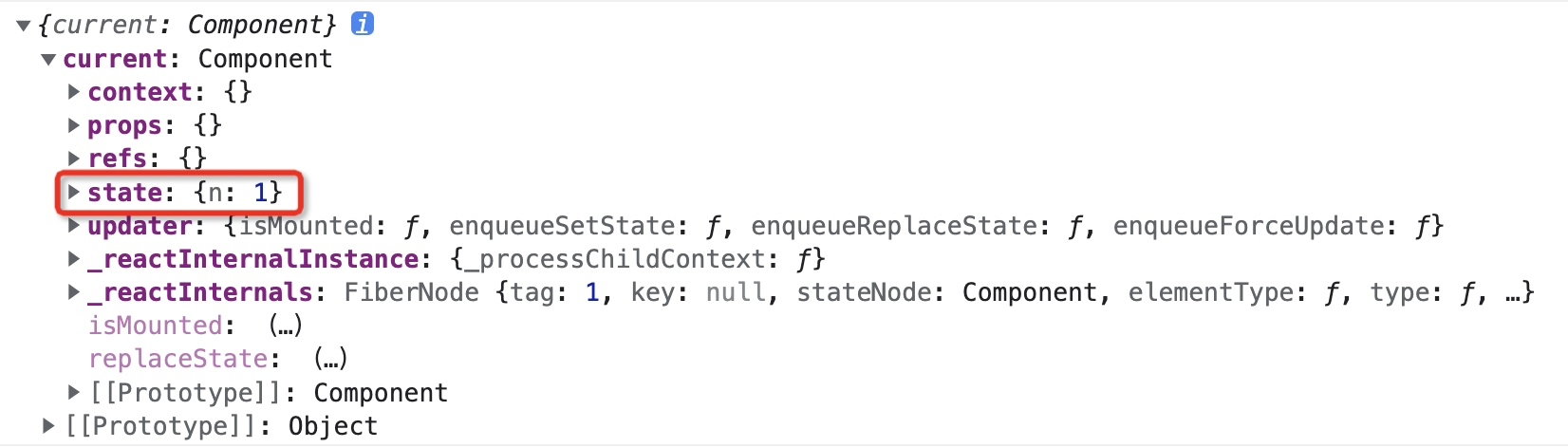
|
||||
|
||||
要解决这个问题就会涉及到 *Ref* 的转发。说直白一点就是 *Ref* 的向下传递给子组件。
|
||||
|
||||
这里 *React* 官方为我们提供了一个 *React.forwardRef API*。我们需要修改的仅仅是高阶组件:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools";
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withLog(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
class WithLogCom extends Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = { n: 1 };
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentDidMount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentWillUnmount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
// 通过 this.props 能够拿到传递下来的 ref
|
||||
// 然后和子组件进行关联
|
||||
const {forwardedRef, ...rest} = this.props;
|
||||
return <Com ref={forwardedRef} {...rest} />;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {
|
||||
// 这里是关键,渲染函数会自动传入 ref,然后我们将 ref 继续往下传递
|
||||
return <WithLogCom {...props} forwardedRef={ref} />;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withLog;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,*React.forwardRef* 接受一个渲染函数,该函数接收 *props* 和 *ref* 参数并返回原本我们直接返回的增强组件。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们在增强组件的 *render* 方法中,通过 *this.props* 拿到 *ref* 继续传递给子组件。
|
||||
|
||||
那么 *React.forwardRef* 究竟做了啥呢?源码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055526.png" alt="image-20221130135525552" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,实际上 *forwardRef* 这个静态方法实际上也就是返回一个 *elementType* 的对象而已,该对象包含一个 *render* 方法,也就是我们在使用 *React.forwardRef* 时传入的渲染函数。
|
||||
|
||||
之所以要这么多此一举,是因为该渲染函数会自动传入 *props* 和 *ref*,关键点就在这里,拿到 *ref* 后,后我们就可以将 *ref* 继续往下面传递给子组件。
|
||||
|
||||
## *useRef* 与 *useImperativeHandle*
|
||||
|
||||
关于 *Ref* 这一块,最后要看一下的就是这两个 *Hook*。
|
||||
|
||||
我们知道,现在整个 *React* 是函数组件大行其道,那么自然我们会遇到函数组件下如何进行 *Ref* 的关联。
|
||||
|
||||
在函数组件中,官方为我们提供了新的 *useRef* 这个 *Hook*来进行关联,但是也可以使用 *createRef API*,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = React.useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
const inputRef1 = React.createRef();
|
||||
const inputRef2 = React.useRef();
|
||||
console.log("inputRef1:", inputRef1); // {current: null}
|
||||
console.log("inputRef2:", inputRef2); // {current: undefined}
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle() {
|
||||
console.log("inputRef1:", inputRef1); // {current: input}
|
||||
console.log("inputRef2:", inputRef2); // {current: input}
|
||||
setCounter(counter + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onClick={clickHandle}>+1</button>
|
||||
<div>{counter}</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<input type="text" ref={inputRef1} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<input type="text" ref={inputRef2} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上面的示例我们可以看出,虽然 *createRef* 和 *useRef* 都是创建 *Ref* 的,但是还是有一些区别,主要体现在下面的点:
|
||||
|
||||
- *useRef* 是 *hooks* 的一种,一般用于 *function* 组件,而 *createRef* 一般用于 *class* 组件
|
||||
|
||||
- 由 *useRef* 创建的 *ref* 对象在组件的整个生命周期内都不会改变,但是由 *createRef* 创建的 *ref* 对象,组件每更新一次,*ref*对象就会被重新创建
|
||||
|
||||
实际上,就是因为在函数式组件中使用 *createRef* 创建 *ref* 时存在弊端,组件每次更新,*ref* 对象就会被重新创建,所以出现了 *useRef* 来解决这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
*useRef* 还接受一个初始值,这在用作关联 *DOM* 元素时通常没什么用,但是在作为**存储不需要变化**的全局变量时则非常方便。来看下面的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
let timer;
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
timer = setInterval(() => {
|
||||
console.log('触发了');
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
},[]);
|
||||
|
||||
const clearTimer = () => {
|
||||
clearInterval(timer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle(){
|
||||
console.log(timer);
|
||||
setCounter(counter + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<>
|
||||
<div>{counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={clickHandle}>+1</button>
|
||||
<button onClick={clearTimer}>停止</button>
|
||||
</>)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的写法存在一个问题,如果这个 *App* 组件里有 *state* 变化或者他的父组件重新 *render* 等原因导致这个 *App* 组件重新 *render* 的时候,我们会发现,点击停止按钮,定时器依然会不断的在控制台打印,定时器清除事件无效了。
|
||||
|
||||
因为组件重新渲染之后,这里的 *timer* 以及 *clearTimer* 方法都会重新创建,*timer* 已经不是存储的之前的定时器的变量了。
|
||||
|
||||
此时根据 *useRef* 在组件的整个生命周期内都不会改变的特性,我们可以将定时器变量存储到 *useRef* 所创建的对象上面,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState, useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
let timer = useRef(null);
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
timer.current = setInterval(() => {
|
||||
console.log('触发了');
|
||||
}, 1000);
|
||||
},[]);
|
||||
|
||||
const clearTimer = () => {
|
||||
clearInterval(timer.current);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle(){
|
||||
console.log(timer);
|
||||
setCounter(counter + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<>
|
||||
<div>{counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={clickHandle}>+1</button>
|
||||
<button onClick={clearTimer}>停止</button>
|
||||
</>)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们要看一下另外一个 *useImperativeHandle* 这个 *Hook*。
|
||||
|
||||
该 *Hook* 一般配合 *React.forwardRef* 使用,主要作用是父组件传入 *Ref* 时,**自定义**要暴露给父组件的实例值。
|
||||
|
||||
来看一个具体的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import {useRef} from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const comRef = useRef();
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle(){
|
||||
comRef.current.click();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 ref={comRef}/>
|
||||
<button onClick={clickHandle}>触发子组件的方法</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在父组件中,我们向子组件传递了一个 *Ref*,但是子组件实际上是一个函数组件。之前我们有说过,函数组件本身是无法挂 *Ref* 的,因此此时就需要使用 *React.forwardRef* 进行 *Ref* 的转发,之后配合 *useImperativeHandle* 来自定义要暴露给父组件的实例值。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { useRef, useImperativeHandle } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props, ref) {
|
||||
|
||||
const childRef = useRef();
|
||||
|
||||
// 第一个是父组件传递过来的 ref
|
||||
// 第二个回调函数返回一个对象,该对象是一个映射关系
|
||||
// 映射关系中的键之后能够暴露给父组件使用
|
||||
// 映射关系中的值对应的是对应的方法
|
||||
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
|
||||
click: () => {
|
||||
console.log(childRef.current);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}));
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle() {
|
||||
console.log("这是子组件的 test 方法");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div onClick={clickHandle} ref={childRef}>
|
||||
子组件1
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要做 ref 转发
|
||||
export default React.forwardRef(ChildCom1);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们使用了 *useImperativeHandle* 这个 *Hook*,该 *Hook* 的第一个参数是父组件传递进来的 *ref*,第二个回调函数返回一个对象,该对象是一个映射关系,映射关系中的键之后能够暴露给父组件使用,映射关系中的值对应的是对应的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
17
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
20
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.jsx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
import ChildCom from "./components/ChildCom";
|
||||
import { useRef } from "react";
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const comRef = useRef();
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle(){
|
||||
comRef.current.click();
|
||||
comRef.current.testHandle();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<>
|
||||
<ChildCom ref={comRef} />
|
||||
<button onClick={clickHandle}>click</button>
|
||||
</>)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
43
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/src/HOC/withLog.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
// withLog.js
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools";
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withLog(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
class WithLogCom extends React.Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = { n: 1 };
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentDidMount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentWillUnmount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
const { forwardRef, ...rest } = this.props;
|
||||
return <Com ref={forwardRef} {...rest} />;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {
|
||||
// props 就是上一层传递进来的属性
|
||||
// ref 就是上一层传递进来的 ref
|
||||
return <WithLogCom {...props} forwardRef={ref} />;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withLog;
|
||||
29
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/src/components/ChildCom.jsx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
import React, { useRef, useImperativeHandle } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom(props, ref) {
|
||||
|
||||
const childRef = useRef();
|
||||
|
||||
// 自定义使用 ref 时向父组件要暴露的东西
|
||||
// 第一个是父组件传递过来的 ref
|
||||
// 第二个参数是一个回调函数,该函数返回一个对象
|
||||
// 这个对象里面就定义映射关系,也就是具体要向父组件暴露的东西
|
||||
useImperativeHandle(ref,()=>({
|
||||
click : () => {
|
||||
console.log(childRef.current)
|
||||
},
|
||||
testHandle : test
|
||||
}))
|
||||
|
||||
function test(){
|
||||
console.log("这是子组件的test方法");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div ref={childRef}>
|
||||
子组件
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default React.forwardRef(ChildCom);
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
80
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-3. Ref/课堂代码/my-app/src/utils/tools.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 格式化时间戳
|
||||
* @param {*} timestamp
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export function formatDate(timestamp, part) {
|
||||
if (!timestamp) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let date = new Date(parseInt(timestamp));
|
||||
|
||||
let year = date.getFullYear(); // 年
|
||||
let month = date.getMonth() + 1; // 月
|
||||
let day = date.getDate(); // 日
|
||||
|
||||
let hour = date.getHours(); // 时
|
||||
let minutes = date.getMinutes(); // 分
|
||||
let seconds = date.getSeconds(); // 秒
|
||||
|
||||
let weekArr = [
|
||||
"星期日",
|
||||
"星期一",
|
||||
"星期二",
|
||||
"星期三",
|
||||
"星期四",
|
||||
"星期五",
|
||||
"星期六",
|
||||
];
|
||||
let week = weekArr[date.getDay()];
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要给一位数前面加 0
|
||||
// 9 点 ----> 09:45:03
|
||||
|
||||
if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) {
|
||||
// month += '0'; // a += b ----> a = a + b
|
||||
month = "0" + month;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (day >= 0 && day <= 9) {
|
||||
day = "0" + day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (hour >= 0 && hour <= 9) {
|
||||
hour = "0" + hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minutes >= 0 && minutes <= 9) {
|
||||
minutes = "0" + minutes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (seconds >= 0 && seconds <= 9) {
|
||||
seconds = "0" + seconds;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var str = "";
|
||||
|
||||
switch (part) {
|
||||
case "year": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} `;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "year-time": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time-week": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
429
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课件资料/4. Context.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,429 @@
|
||||
# 4. *Context*
|
||||
|
||||
有关 *Context*,这是一个非常重要的知识点,甚至我们之后在书写 *mini-react、mini-react-router、mini-redux* 时都会用到的一个知识点,所以这一小节,我们就来好好看一下 *Context* 的相关内容,主要包含以下几个点:
|
||||
|
||||
- *Context* 要解决的问题
|
||||
- *Context* 的用法
|
||||
- *Context* 相关 *Hook*
|
||||
|
||||
## *Context* 要解决的问题
|
||||
|
||||
首先来看一下 *Context* 要解决的问题。正常来讲,我们单页应用中的组件会形成一个像组件树一样结构,当内部组件和组件之间要进行数据传递时,就免不了一层一层先传递到共同的父组件,然后再一层一层传递下去。
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055702.png" alt="image-20221130135702192" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
假设 *subComA-1* 组件的状态数据要传递给 *subComB-2* 组件,应该怎么做?
|
||||
|
||||
根据我们前面所讲的单项数据流的规则,那么数据应该被提升到 *App* 根组件,然后通过 *props* 一层一层的传递给下面的子组件,最终 *subComA-1* 拿到所需要的数据;如果 *subComA-1* 组件需要修改传递下来的数据,那么该组件就还需接收从 *App* 根组件一层一层传递下来的能够修改数据的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
官方在“何时使用 *Context*”这一小节也举了一个形象的例子:
|
||||
*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/context.html#when-to-use-context*
|
||||
|
||||
因此,简单一句话概括 *Context*,那就是解决组件之间数据共享的问题,避免一层一层的传递。
|
||||
|
||||
此时你肯定会想,前面的 *redux* 不就已经解决了这个问题么?没错,实际上 *redux* 的实现原理就是基于 *Context* 所进行的一层封装。
|
||||
|
||||
*Context* 如果直接翻译成中文,会被翻译成“上下文”,这其实在软件领域很常见的一个词,比如前面我们也学习过“执行上下文”,所谓上下文,往往指的是代码执行时所需的**数据环境信息**。
|
||||
|
||||
>实际上生活中也有类似的场景,例如你在厨房做饭,你的周围有各种做饭所需的厨具,例如菜刀、案板、锅、瓢等,这些工具构成了一个(上下文)环境,当你要做饭要用到某一样工具时,直接从这个环境中就能过获取到。
|
||||
>
|
||||
><img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055752.png" alt="image-20221130135751769" style="zoom:40%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
## *Context* 的用法
|
||||
|
||||
*React* 官方对于 *Context* 的用法,分为旧版 *API* 和新版 *API*,有关旧版 *API* 的用法,本文档就不再赘述,如果有需要的同学,可以参阅:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/legacy-context.html*
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们来看一下新版 *API* 的使用,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// src/context/index.js
|
||||
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
const MyContext = React.createContext();
|
||||
export default MyContext;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用 *React.createContext API* 创建的一个上下文对象,该对象里面会提供两个组件,分别是 *Provider* 和 *Consumer*,表示数据的提供者和消费者。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// App.jsx
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import MyContext from "./context";
|
||||
import { useState } from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
const { Provider } = MyContext;
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<Provider value={{ count, setCount }}>
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "250px",
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</Provider>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在根组件 *App.jsx* 中,我们设置了一个根组件的状态数据 *count*,然后从 *MyContext* 中解构出 *Provider* 组件来作为数据的提供者,*value* 属性用来设置要提供的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// components/ChildCom1.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./ChildCom2"
|
||||
import ChildCom3 from "./ChildCom3"
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<ChildCom2/>
|
||||
<ChildCom3/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 *ChildCom1* 子组件中,无需再像中转站一样接受父组件的数据然后又传递给 *ChildCom2* 和 *ChildCom3* 组件。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// components/ChildCom2.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import MyContext from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
const { Consumer } = MyContext;
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<Consumer>
|
||||
{(context) => (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
onClick={() => context.setCount(context.count + 1)}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom2
|
||||
<div>count:{context.count}</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</Consumer>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*ChildCom2* 组件是一个函数组件,函数组件想要获取 *Context* 上下文中的数据,需要使用 *Consumer* 组件,这种方法需要一个函数作为子元素,这个函数接收当前的 *context* 值,并返回一个 *React* 节点。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
import MyContext from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ChildCom3 extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
static contextType = MyContext;
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
onClick={()=>this.context.setCount(this.context.count + 2)}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom3
|
||||
<div>count:{this.context.count}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*ChildCom3* 组件是一个类组件,类组件当然也可以使用上面 *Consumer* 的方式来获取上下文中的数据,但对于类组件而言,还可以使用 *contextType* 的方式。挂载在 *class* 上的 *contextType* 属性可以赋值为由 *React.createContext( )* 创建的 *Context* 对象。
|
||||
|
||||
整体的组件树结构图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055829.png" alt="image-20221130135829210" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
最后我们来看一下效果:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### *displayName*
|
||||
|
||||
如果安装了 *React Developer Tools* 工具,那么在 *components* 选项卡中可以看到如下的组件树结构,默认的名字就为 *Context.Provider* 和 *Context.Consumer*
|
||||
|
||||
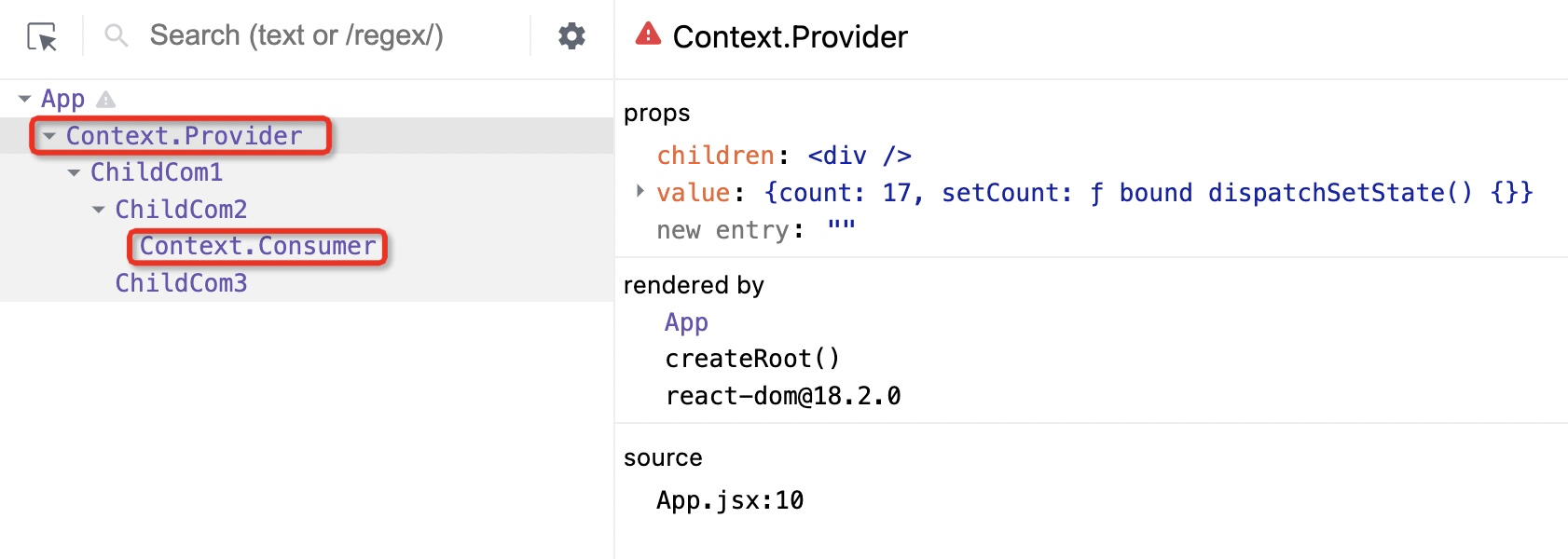
|
||||
|
||||
通过设置 *displayName* 可以修改显示名字,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
const MyContext = React.createContext();
|
||||
MyContext.displayName = 'counter';
|
||||
export default MyContext;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-055958.png" alt="image-20221130135957667" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认值
|
||||
|
||||
*Context* 上下文环境可以设置默认值,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
const MyContext = React.createContext({
|
||||
name: "xiejie",
|
||||
age: 18,
|
||||
});
|
||||
MyContext.displayName = "counter";
|
||||
export default MyContext;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时就**<u>不再需要 *Provider* 组件来提供数据</u>**了,子组件可以直接消费上下文环境的默认数据。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// App.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "250px",
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
根组件 *App* 已经不再需要使用 *Provider* 组件来提供初始数据。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import MyContext from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
const { Consumer } = MyContext;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<Consumer>
|
||||
{(context) => (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom2
|
||||
<div>name:{context.name}</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</Consumer>
|
||||
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
import MyContext from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ChildCom3 extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
static contextType = MyContext;
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom3
|
||||
<div>age:{this.context.age}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
无论是 *ChildCom2* 还是 *ChildCom3*,都能够直接从上下文中获取默认的上下文数据。
|
||||
|
||||
效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-060026.png" alt="image-20221130140025242" style="zoom:67%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
### 多个上下文环境
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的示例中,我们示例的都是一个 *Context* 上下文环境,这通常也够用了,但是这并不意味着只能提供一个上下文环境,我们可以创建多个上下文环境,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
export const MyContext1 = React.createContext();
|
||||
export const MyContext2 = React.createContext();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们导出两个上下文环境,接下来在 *App.jsx* 中,使用多个 *Provider* 作为数据的提供者
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import { MyContext1, MyContext2 } from "./context"
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext1.Provider value={{ a: 1, b: 2 }}>
|
||||
<MyContext2.Provider value={{ b: 10, c: 20 }}>
|
||||
<div style={{border: '1px solid',width: "250px",}}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</MyContext2.Provider>
|
||||
</MyContext1.Provider>
|
||||
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后在 *ChildCom2* 和 *ChildCom3* 中同样也使用多个 *Consumer* 来消费不同上下文中的数据
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import { MyContext1, MyContext2 } from "../context";
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
{
|
||||
(context1) => (
|
||||
<MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
{(context2) => (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom2
|
||||
<div>a : {context1.a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b : {context1.b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c : {context2.c}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
</MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
import { MyContext1, MyContext2 } from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ChildCom3 extends Component {
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
{
|
||||
(context1) => (
|
||||
<MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
{
|
||||
(context2) => (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom3
|
||||
<div>a:{context1.a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b:{context2.b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c:{context2.c}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
</MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
</MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-11-30-060047.png" alt="image-20221130140046232" style="zoom:67%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
>在消费上下文里面的数据时,如果回调函数中的参数名相同,则从最近的上下文中去获取数据。
|
||||
|
||||
## *Context* 相关 *Hook*
|
||||
|
||||
在 *React Hook API* 中,为我们提供了一个更加方便的 *useContext* 钩子函数,该 *Hook* 接收一个由 *React.createContext API* 创建的上下文对象,并返回该 *context* 的当前值。
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useContext } from 'react';
|
||||
import { MyContext1 } from "../context";
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
const { a, b, c } = useContext(MyContext1)
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom2
|
||||
<div>a : {a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b : {b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c : {c}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*useContext(MyContext)* 相当于类组件中的 *static contextType = MyContext* 或者 \<*MyContext.Consumer*>,但是我们**<u>仍然需要在上层组件树中使用 \<*MyContext.Provider*> 来为下层组件提供 *context*</u>**。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
17
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
24
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.jsx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import { MyContext1, MyContext2 } from "./context";
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
// 这是我在根组件维护的状态数据
|
||||
// const [counter, setCounter] = useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
// 这里的 value 相当于是将后面的数据放入到上下文环境中
|
||||
<MyContext1.Provider value={{ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }}>
|
||||
<MyContext2.Provider value={{ a: 100, b: 200, c: 300 }}>
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "250px",
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</MyContext2.Provider>
|
||||
</MyContext1.Provider>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
43
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/src/HOC/withLog.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
// withLog.js
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools";
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withLog(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
class WithLogCom extends React.Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = { n: 1 };
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentDidMount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentWillUnmount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
const { forwardRef, ...rest } = this.props;
|
||||
return <Com ref={forwardRef} {...rest} />;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {
|
||||
// props 就是上一层传递进来的属性
|
||||
// ref 就是上一层传递进来的 ref
|
||||
return <WithLogCom {...props} forwardRef={ref} />;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withLog;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./ChildCom2";
|
||||
import ChildCom3 from "./ChildCom3";
|
||||
import ChildCom4 from "./ChildCom4";
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<ChildCom2 />
|
||||
<ChildCom3 />
|
||||
<ChildCom4 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import { MyContext1, MyContext2 } from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
{(context1) => {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
{(context2) => (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom2
|
||||
<div>a:{context1.a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b:{context1.b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c:{context1.c}</div>
|
||||
<div>a:{context2.a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b:{context2.b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c:{context2.c}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
</MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import { MyContext1, MyContext2 } from "../context";
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom3() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
{(context) => {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
{(context) => (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom3
|
||||
<div>a:{context.a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b:{context.b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c:{context.c}</div>
|
||||
<div>a:{context.a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b:{context.b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c:{context.c}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</MyContext2.Consumer>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
</MyContext1.Consumer>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom3;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
import { useContext } from 'react';
|
||||
import { MyContext1 } from "../context"
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom4() {
|
||||
|
||||
const { a, b, c } = useContext(MyContext1);
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid',
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
userSelect: 'none'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
ChildCom4
|
||||
<div>a:{a}</div>
|
||||
<div>b:{b}</div>
|
||||
<div>c:{c}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom4;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
|
||||
export const MyContext1 = React.createContext(); // 上下文对象
|
||||
export const MyContext2 = React.createContext(); // 上下文对象
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
80
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-4. Context/课堂代码/my-app/src/utils/tools.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 格式化时间戳
|
||||
* @param {*} timestamp
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export function formatDate(timestamp, part) {
|
||||
if (!timestamp) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let date = new Date(parseInt(timestamp));
|
||||
|
||||
let year = date.getFullYear(); // 年
|
||||
let month = date.getMonth() + 1; // 月
|
||||
let day = date.getDate(); // 日
|
||||
|
||||
let hour = date.getHours(); // 时
|
||||
let minutes = date.getMinutes(); // 分
|
||||
let seconds = date.getSeconds(); // 秒
|
||||
|
||||
let weekArr = [
|
||||
"星期日",
|
||||
"星期一",
|
||||
"星期二",
|
||||
"星期三",
|
||||
"星期四",
|
||||
"星期五",
|
||||
"星期六",
|
||||
];
|
||||
let week = weekArr[date.getDay()];
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要给一位数前面加 0
|
||||
// 9 点 ----> 09:45:03
|
||||
|
||||
if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) {
|
||||
// month += '0'; // a += b ----> a = a + b
|
||||
month = "0" + month;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (day >= 0 && day <= 9) {
|
||||
day = "0" + day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (hour >= 0 && hour <= 9) {
|
||||
hour = "0" + hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minutes >= 0 && minutes <= 9) {
|
||||
minutes = "0" + minutes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (seconds >= 0 && seconds <= 9) {
|
||||
seconds = "0" + seconds;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var str = "";
|
||||
|
||||
switch (part) {
|
||||
case "year": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} `;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "year-time": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time-week": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
329
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课件资料/5. Render Props.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,329 @@
|
||||
# 5. *Render Props*
|
||||
|
||||
在 *React* 中,代码复用的最基本单位就是组件,但是如果组件中也出现了重复的代码,该怎么做呢?
|
||||
|
||||
那么我们需要通过某种方式将代码中公共的部分抽取出来,这些公共的部分就被称之为横切关注点(*Cross-Cutting Concerns*)
|
||||
|
||||
在 *React* 中,常见有两种方式来进行横切关注点的抽离:
|
||||
|
||||
- 高阶组件(*HOC*)
|
||||
- *Render Props*
|
||||
|
||||
*Render Props* 实际上**<u>本身并非什么新语法</u>**,而是指一种在 *React* 组件之间**<u>使用一个值为函数的 *prop* 共享代码</u>**的简单技术。
|
||||
|
||||
有关 *Render Props*,咱们主要需要掌握以下 *2* 个点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 如何用?
|
||||
- 何时用?
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何使用 *Render Props*
|
||||
|
||||
我们首先还是来看一个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// App.jsx
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
display: 'flex',
|
||||
justifyContent: 'space-between',
|
||||
width: "850px"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
<ChildCom2 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// components/ChildCom1.jsx
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [points, setPoints] = useState({
|
||||
x: 0,
|
||||
y: 0
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
function handleMouseMove(e) {
|
||||
setPoints({
|
||||
x: e.clientX,
|
||||
y: e.clientY
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '400px',
|
||||
height: '400px',
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'red'
|
||||
}} onMouseMove={handleMouseMove}>
|
||||
<h1>移动鼠标!</h1>
|
||||
<p>当前的鼠标位置是 ({points.x}, {points.y})</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// components/ChildCom2.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [points, setPoints] = useState({
|
||||
x: 0,
|
||||
y: 0
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
function handleMouseMove(e) {
|
||||
setPoints({
|
||||
x: e.clientX,
|
||||
y: e.clientY
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '400px',
|
||||
height: '400px',
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'grey',
|
||||
position: 'relative',
|
||||
overflow: 'hidden'
|
||||
}} onMouseMove={handleMouseMove}>
|
||||
<h1>移动鼠标!</h1>
|
||||
{/* 这里减去 460 是因为要减去左边 div 的宽度 + 两个大 div 之间 50 的间距 */}
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '15px',
|
||||
height: '15px',
|
||||
borderRadius: "50%",
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'white',
|
||||
position: 'absolute',
|
||||
left: points.x - 5 - 460,
|
||||
top: points.y - 5 - 10,
|
||||
}}></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,*App* 根组件下渲染了两个子组件,这两个子组件一个是显示鼠标的位置,另外一个是根据鼠标位置显示一个追随鼠标移动的小球。
|
||||
|
||||
仔细观察代码,你会发现这两个子组件内部的逻辑基本上是一模一样的,只是最终渲染的内容不一样,此时我们就可以使用 *Render Props* 对横切关注点进行一个抽离。
|
||||
|
||||
方式也很简单,就是在一个组件中使用一个值为函数的 *prop*,函数的返回值为要渲染的视图。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// /components/MouseMove.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function MouseMove(props) {
|
||||
const [points, setPoints] = useState({
|
||||
x: 0,
|
||||
y: 0
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
function handleMouseMove(e) {
|
||||
setPoints({
|
||||
x: e.clientX,
|
||||
y: e.clientY
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
props.render ? props.render({ points, handleMouseMove }) : null
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default MouseMove;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们新创建了一个 *MouseMove* 组件,该组件就封装了之前 *ChildCom1* 和 *ChildCom2* 组件的公共逻辑。该组件的 *props* 接收一个名为 *render* 的参数,只不过该参数对应的值为一个函数,我们调用时将对应的状态和处理函数传递过去,该函数的调用结果为返回一段视图。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2";
|
||||
import MouseMove from "./components/MouseMove";
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
display: 'flex',
|
||||
justifyContent: 'space-between',
|
||||
width: "850px"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<MouseMove render={props => <ChildCom1 {...props} />} />
|
||||
<MouseMove render={props => <ChildCom2 {...props} />} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来在 *App* 根组件中,我们使用 *MouseMove* 组件,该组件上有一个 *render* 属性,对应的值就是函数,函数返回要渲染的组件。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '400px',
|
||||
height: '400px',
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'red'
|
||||
}} onMouseMove={props.handleMouseMove}>
|
||||
<h1>移动鼠标!</h1>
|
||||
<p>当前的鼠标位置是 ({props.points.x}, {props.points.y})</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function ChildCom2(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '400px',
|
||||
height: '400px',
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'grey',
|
||||
position: 'relative',
|
||||
overflow: 'hidden'
|
||||
}} onMouseMove={props.handleMouseMove}>
|
||||
<h1>移动鼠标!</h1>
|
||||
{/* 这里减去 460 是因为要减去左边 div 的宽度 + 两个大 div 之间 50 的间距 */}
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '15px',
|
||||
height: '15px',
|
||||
borderRadius: "50%",
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'white',
|
||||
position: 'absolute',
|
||||
left: props.points.x - 5 - 460,
|
||||
top: props.points.y - 5 - 10,
|
||||
}}></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最后就是子组件 *ChildCom1* 和 *ChildCom2* 的改写,可以看到这两个子组件就只需要书写要渲染的视图了。公共的逻辑已经被 *MouseMove* 抽取出去了。
|
||||
|
||||
另外需要说明的是,虽然这个技巧的名字叫做 *Render Props*,但不是说必须要提供一个名为 *render* 的属性,事实上,**<u>封装公共逻辑的组件(例如上面的 *MouseMove*)只要能够得到要渲染的视图即可</u>**,所以传递的方式可以有多种。
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2";
|
||||
import MouseMove from "./components/MouseMove";
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
display: 'flex',
|
||||
justifyContent: 'space-between',
|
||||
width: "850px"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<MouseMove>
|
||||
{(props) => <ChildCom1 {...props} />}
|
||||
</MouseMove>
|
||||
<MouseMove>
|
||||
{props => <ChildCom2 {...props} />}
|
||||
</MouseMove>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面使用 *MouseMove* 组件时,并没有传递什么 *render* 属性,而是通过 *props.children* 的形式将要渲染的视图传递到了组件内部。
|
||||
|
||||
在 *MouseMove* 组件内部,就不再是执行 *render* 方法了,而是应该执行 *props.children*,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
props.children ? props.children({ points, handleMouseMove }) : null
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 何时使用 *Render Props*
|
||||
|
||||
知道了 *Render Props* 的使用方法后,接下来我们来看一下何时使用 *Render Props*。
|
||||
|
||||
同样是作为抽离横切关注点,前面所讲的 *HOC* 也能做到相同的效果。例如我们可以将上面的示例修改为 *HOC* 的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// HOC/withMouseMove.js
|
||||
|
||||
import { useState } from "react";
|
||||
function withMouseMove(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回一个新组件
|
||||
return function NewCom() {
|
||||
const [points, setPoints] = useState({
|
||||
x: 0,
|
||||
y: 0,
|
||||
});
|
||||
function handleMouseMove(e) {
|
||||
setPoints({
|
||||
x: e.clientX,
|
||||
y: e.clientY,
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const mouseHandle = { points, handleMouseMove };
|
||||
return <Com {...mouseHandle} />;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withMouseMove;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// App.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2";
|
||||
import withMouseMove from "./HOC/withMouseMove"
|
||||
|
||||
const NewChildCom1 = withMouseMove(ChildCom1);
|
||||
const NewChildCom2 = withMouseMove(ChildCom2);
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
display: 'flex',
|
||||
justifyContent: 'space-between',
|
||||
width: "850px"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<NewChildCom1 />
|
||||
<NewChildCom2 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
那么自然而然疑问就来了,什么时候使用 *Render Props* ?什么时候使用 *HOC* ?
|
||||
|
||||
一般来讲,**<u>*Render Props* 应用于组件之间功能逻辑完全相同,仅仅是渲染的视图不同</u>**。这个时候我们可以通过 *Render Props* 来指定要渲染的视图是什么。
|
||||
|
||||
而 *HOC* 一般是抽离部分公共逻辑,也就是说组件之间有一部分逻辑相同,但是各自也有自己独有的逻辑,那么这个时候使用 *HOC* 比较合适,可以在原有的组件的基础上做一个增强处理。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
17
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
40
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.jsx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2";
|
||||
// import MouseMove from "./components/MouseMove";
|
||||
|
||||
import withMouseMove from "./HOC/withMouseMove"
|
||||
|
||||
const NewChildCom1 = withMouseMove(ChildCom1);
|
||||
const NewChildCom2 = withMouseMove(ChildCom2);
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
display: 'flex',
|
||||
justifyContent: 'space-between',
|
||||
width: "850px"
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
{/* 这边就不再是直接使用 ChildCom1、ChildCom2 */}
|
||||
{/* <ChildCom1 />
|
||||
<ChildCom2 /> */}
|
||||
{/* 改为使用 MouseMove */}
|
||||
{/* MouseMove 的 render 这个 props 属性对应的值是一个函数
|
||||
该函数表明了我要渲染的视图 */}
|
||||
{/* <MouseMove>
|
||||
{(props) => <ChildCom1 {...props} />}
|
||||
</MouseMove>
|
||||
<MouseMove>
|
||||
{(props) => <ChildCom2 {...props} />}
|
||||
</MouseMove> */}
|
||||
|
||||
{/* 下面是使用高阶组件的方式 */}
|
||||
<NewChildCom1/>
|
||||
<NewChildCom2/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
43
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/src/HOC/withLog.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
// withLog.js
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
import { formatDate } from "../utils/tools";
|
||||
|
||||
// 高阶组件是一个函数,接收一个组件作为参数
|
||||
// 返回一个新的组件
|
||||
function withLog(Com) {
|
||||
// 返回的新组件
|
||||
class WithLogCom extends React.Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = { n: 1 };
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentDidMount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经创建,创建时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
componentWillUnmount() {
|
||||
console.log(
|
||||
`日志:组件${Com.name}已经销毁,销毁时间${formatDate(
|
||||
Date.now(),
|
||||
"year-time"
|
||||
)}`
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
const { forwardRef, ...rest } = this.props;
|
||||
return <Com ref={forwardRef} {...rest} />;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {
|
||||
// props 就是上一层传递进来的属性
|
||||
// ref 就是上一层传递进来的 ref
|
||||
return <WithLogCom {...props} forwardRef={ref} />;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withLog;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
import { useState } from "react";
|
||||
function withMouseMove(Com) {
|
||||
return function NewCom() {
|
||||
const [points, setPoints] = useState({
|
||||
x: 0,
|
||||
y: 0,
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
function mouseMoveHandle(e) {
|
||||
setPoints({
|
||||
x: e.clientX,
|
||||
y: e.clientY,
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const mousemove = { points, mouseMoveHandle };
|
||||
|
||||
return <Com {...mousemove} />;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default withMouseMove;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
|
||||
// 移动鼠标,可以记录当前鼠标的位置
|
||||
// 仔细观察下面的代码,我们会发现两个组件的逻辑一模一样
|
||||
// 仅仅是渲染的视图不一样
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '400px',
|
||||
height: '400px',
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'red'
|
||||
}} onMouseMove={props.mouseMoveHandle}>
|
||||
<h1>移动鼠标</h1>
|
||||
<p>当前鼠标的位置:x {props.points.x} y {props.points.y}</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
// 该组件的效果是一个小球会追随鼠标进行移动
|
||||
function ChildCom2(props) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
width: '400px',
|
||||
height: '400px',
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'grey',
|
||||
position: 'relative',
|
||||
overflow: 'hidden'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
onMouseMove={props.mouseMoveHandle}
|
||||
>
|
||||
<h1>移动鼠标</h1>
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
width: '15px',
|
||||
height: '15px',
|
||||
borderRadius: "50%",
|
||||
backgroundColor: 'white',
|
||||
position: 'absolute',
|
||||
left: props.points.x - 5 - 460,
|
||||
top: props.points.y - 5 - 10,
|
||||
}}
|
||||
></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
// 该组件负责公共的逻辑
|
||||
function MouseMove(props) {
|
||||
|
||||
const [points, setPoints] = useState({
|
||||
x: 0,
|
||||
y: 0
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
function mouseMoveHandle(e) {
|
||||
setPoints({
|
||||
x: e.clientX,
|
||||
y: e.clientY
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
props.children ? props.children({points, mouseMoveHandle}) : null
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default MouseMove;
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
80
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-5. Render Props/课堂代码/my-app/src/utils/tools.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 格式化时间戳
|
||||
* @param {*} timestamp
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export function formatDate(timestamp, part) {
|
||||
if (!timestamp) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let date = new Date(parseInt(timestamp));
|
||||
|
||||
let year = date.getFullYear(); // 年
|
||||
let month = date.getMonth() + 1; // 月
|
||||
let day = date.getDate(); // 日
|
||||
|
||||
let hour = date.getHours(); // 时
|
||||
let minutes = date.getMinutes(); // 分
|
||||
let seconds = date.getSeconds(); // 秒
|
||||
|
||||
let weekArr = [
|
||||
"星期日",
|
||||
"星期一",
|
||||
"星期二",
|
||||
"星期三",
|
||||
"星期四",
|
||||
"星期五",
|
||||
"星期六",
|
||||
];
|
||||
let week = weekArr[date.getDay()];
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要给一位数前面加 0
|
||||
// 9 点 ----> 09:45:03
|
||||
|
||||
if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) {
|
||||
// month += '0'; // a += b ----> a = a + b
|
||||
month = "0" + month;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (day >= 0 && day <= 9) {
|
||||
day = "0" + day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (hour >= 0 && hour <= 9) {
|
||||
hour = "0" + hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minutes >= 0 && minutes <= 9) {
|
||||
minutes = "0" + minutes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (seconds >= 0 && seconds <= 9) {
|
||||
seconds = "0" + seconds;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var str = "";
|
||||
|
||||
switch (part) {
|
||||
case "year": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} `;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "year-time": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time-week": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
153
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课件资料/6. Portals.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
|
||||
# 6. *Portals*
|
||||
|
||||
*Portals* 被翻译成传送门,它要做的事情实际上也确实和传送门很相似,根据官方的解释:
|
||||
|
||||
>*Portal* 提供了一种将子节点渲染到存在于父组件以外的 *DOM* 节点的优秀的方案。
|
||||
|
||||
其语法为:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
ReactDOM.createPortal(child, container)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
第一个参数(*child*)是任何可渲染的 *React* 子元素,第二个参数(*container*)是一个 *DOM* 元素。
|
||||
|
||||
学习一个知识我们仍然是应该从以下 *2* 个点着手:
|
||||
|
||||
- 何时用?
|
||||
- 如何用?
|
||||
|
||||
## 什么场景下需要使用 *Portals*
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们来看一个场景,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// App.jsx
|
||||
import { useState } from "react";
|
||||
import Modal from "./components/Modal"
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [isShow, setIsShow] = useState(false);
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h1>App组件</h1>
|
||||
<button onClick={()=>setIsShow(!isShow)}>显示/隐藏</button>
|
||||
{isShow ? <Modal /> : null}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function Modal() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width : "450px",
|
||||
height : "250px",
|
||||
border : "1px solid",
|
||||
position : "absolute",
|
||||
left : "calc(50% - 225px)",
|
||||
top : "calc(50% - 125px)",
|
||||
textAlign : "center",
|
||||
lineHeight : "250px"
|
||||
}}>模态框</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default Modal;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的示例中,*Modal* 是一个模态框,在 *App* 根组件中能够控制该模态框组件是否显示。
|
||||
|
||||
上面的示例,功能倒是没有什么问题,但是从最终渲染出来的 *html* 结构上来讲,将整个模态框都放在 *root* 这个 *div* 中不是那么合适,我们生成的 *html* 结构上,这个模态框能够渲染到 *modal* 那个 *div* 里面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
并且一旦父组件上面设置了额外的样式,都会影响这个子组件的渲染,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
position: "relative"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<h1>App组件</h1>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setIsShow(!isShow)}>显示/隐藏</button>
|
||||
{isShow ? <Modal /> : null}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们在 *App* 组件中添加一条相对定位的样式,此时我们就会发现由于 *Modal* 是放在整个 *root* 元素里面的,模态框的位置就会收到影响。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,在这种时候,我们就可以使用 *Portals* 来解决这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何使用 *Portals*
|
||||
|
||||
*Portals* 的使用方式也非常简单,只需要使用 *createPortal* 方法来指定渲染到哪个元素中即可。需要注意的是这是和 *React* 渲染相关的,所以 *createPortal* 方法来自于 *react-dom* 这个库。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import {createPortal} from 'react-dom';
|
||||
|
||||
function Modal() {
|
||||
return createPortal((<div style={{
|
||||
width : "450px",
|
||||
height : "250px",
|
||||
border : "1px solid",
|
||||
position : "absolute",
|
||||
left : "calc(50% - 225px)",
|
||||
top : "calc(50% - 125px)",
|
||||
textAlign : "center",
|
||||
lineHeight : "250px"
|
||||
}}>模态框</div>),document.getElementById("modal"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default Modal;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们将要渲染的视图作为 *createPortal* 方法的第一个参数,而第二个参数用于指定要渲染到哪个 *DOM* 元素中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,这一次模态框就被渲染到了 *id* 为 *modal* 的 *div* 中。并且在 *root* 中所设置的样式都不会影响到模态框的显示。
|
||||
|
||||
>其实根据官方的介绍,*Portals* 的典型用例是当父组件有 *overflow: hidden* 或 *z-index* 样式时,但你需要子组件能够在视觉上“跳出”其容器。例如,对话框、悬浮卡以及提示框。
|
||||
|
||||
## 通过 *Portal* 进行事件冒泡
|
||||
|
||||
最后需要注意一下的就是使用 *Portal* 所渲染的元素在触发事件时的冒泡问题。
|
||||
|
||||
以上面的例子为例,看上去模态框已经渲染到了 *modal* 这个元素里面,但是在 *React* 中事件冒泡是按照组件结构来进行冒泡的,我们可以看到即使模态框已经渲染到了 *modal* 里面,但是在组件树中模态框组件仍然是在根组件中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以书写一个例子来验证一下,例如我们为 *App* 根组件绑定一个点击事件,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState } from "react";
|
||||
import Modal from "./components/Modal"
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [isShow, setIsShow] = useState(false);
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
position: "relative"
|
||||
}} onClick={()=>console.log("App 组件被点击了")}>
|
||||
<h1>App组件</h1>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setIsShow(!isShow)}>显示/隐藏</button>
|
||||
{isShow ? <Modal /> : null}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后我们点击模态框,会发现仍然是能够触发 *App* 根组件的点击事件。
|
||||
|
||||
正如官方文档所说:
|
||||
|
||||
>尽管 *portal* 可以被放置在 *DOM* 树中的任何地方,但在任何其他方面,其行为和普通的 *React* 子节点行为一致。由于 *portal* 仍存在于 *React* 树, 且与 *DOM* 树中的位置无关,那么无论其子节点是否是 *portal*,像 *context* 这样的功能特性都是不变的。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>这包含事件冒泡。一个从 *portal* 内部触发的事件会一直冒泡至包含 *React* 树的祖先,即便这些元素并不是 *DOM* 树中的祖先。
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
18
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
<div id="modal"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
19
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.jsx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
import Modal from "./components/Modal"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [isShow, setIsShow] = useState(false);
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
position: 'relative'
|
||||
}} onClick={()=>console.log("App 组件被点击了")}>
|
||||
<h1>App 组件</h1>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setIsShow(!isShow)}>显示/隐藏</button>
|
||||
{isShow ? <Modal /> : null}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
// 弹出框
|
||||
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import { createPortal } from 'react-dom';
|
||||
|
||||
function Modal() {
|
||||
// 之前是直接返回的一段 JSX
|
||||
// 那么现在我们就通过 Portals 来指定这段 JSX 渲染到哪里
|
||||
return createPortal((
|
||||
<div
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
width: "450px",
|
||||
height: "250px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid",
|
||||
position: "absolute",
|
||||
left: "calc(50% - 225px)",
|
||||
top: "calc(50% - 125px)",
|
||||
textAlign: "center",
|
||||
lineHeight: "250px"
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
模态框
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
), document.getElementById("modal"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default Modal;
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
80
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-6. Portals/课堂代码/my-app/src/utils/tools.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 格式化时间戳
|
||||
* @param {*} timestamp
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export function formatDate(timestamp, part) {
|
||||
if (!timestamp) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let date = new Date(parseInt(timestamp));
|
||||
|
||||
let year = date.getFullYear(); // 年
|
||||
let month = date.getMonth() + 1; // 月
|
||||
let day = date.getDate(); // 日
|
||||
|
||||
let hour = date.getHours(); // 时
|
||||
let minutes = date.getMinutes(); // 分
|
||||
let seconds = date.getSeconds(); // 秒
|
||||
|
||||
let weekArr = [
|
||||
"星期日",
|
||||
"星期一",
|
||||
"星期二",
|
||||
"星期三",
|
||||
"星期四",
|
||||
"星期五",
|
||||
"星期六",
|
||||
];
|
||||
let week = weekArr[date.getDay()];
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要给一位数前面加 0
|
||||
// 9 点 ----> 09:45:03
|
||||
|
||||
if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) {
|
||||
// month += '0'; // a += b ----> a = a + b
|
||||
month = "0" + month;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (day >= 0 && day <= 9) {
|
||||
day = "0" + day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (hour >= 0 && hour <= 9) {
|
||||
hour = "0" + hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minutes >= 0 && minutes <= 9) {
|
||||
minutes = "0" + minutes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (seconds >= 0 && seconds <= 9) {
|
||||
seconds = "0" + seconds;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var str = "";
|
||||
|
||||
switch (part) {
|
||||
case "year": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} `;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "year-time": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time-week": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
178
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课件资料/7. 错误边界.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
|
||||
# 7. 错误边界
|
||||
|
||||
这是从 *React 16* 引入了一个新的概念,为了解决的问题就是一个组件出错不至于整个应用崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们还是来看一个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<ChildCom1/>
|
||||
<ChildCom2/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom3 from "./ChildCom3";
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "300px",
|
||||
height: "300px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<ChildCom3 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function getData() {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function ChildCom3() {
|
||||
const arr = getData();
|
||||
const spanContent = arr.map(it => <span>{it}</span>)
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "100px",
|
||||
height: "100px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom3
|
||||
<div>{spanContent}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom3;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "300px",
|
||||
height: "300px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>ChildCom2</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们整个组件树结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-12-08-065452.png" alt="image-20221208145452107" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,*ChildCom1* 下面的 *ChildCom3* 存在问题,这一个组件的问题会导致整个应用崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
**<u>这在某些场景下,实际上是没有必要的,例如有问题的组件是广告、或者一些无关紧要的组件,此时我们就期望渲染出问题组件以外的组件树。</u>**
|
||||
|
||||
错误边界就是用来解决这个问题的。
|
||||
|
||||
>错误边界是一种 *React* 组件,这种组件可以捕获发生在其子组件树任何位置的 *JavaScript* 错误,并打印这些错误,同时展示降级 *UI*,而并不会渲染那些发生崩溃的子组件树。错误边界可以捕获发生在整个子组件树的渲染期间、生命周期方法以及构造函数中的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// components/ErrorBoundary.jsx
|
||||
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = { hasError: false };
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
|
||||
// 更新 state 使下一次渲染能够显示降级后的 UI
|
||||
return { hasError: true };
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
|
||||
// 你同样可以将错误日志上报给服务器
|
||||
console.log("error>>>", error)
|
||||
console.log("errorInfo>>>", errorInfo)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
if (this.state.hasError) {
|
||||
// 你可以自定义降级后的 UI 并渲染
|
||||
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return this.props.children;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们就创建了一个错误边界组件,该组件有一个 *getDerivedStateFromError* 静态方法以及 *componentDidCatch* 实例方法,这两个方法都会在组件渲染出错时调用,但是略有区别,具体的区别如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- *getDerivedStateFromError* 静态方法
|
||||
- 运行时间点:渲染子组件的过程中,发生错误之后,在更新页面之前(整个应用没有崩溃,直接渲染降级 UI)
|
||||
- **注意:只有子组件发生错误,才会运行该函数**
|
||||
- 该函数返回一个对象,*React* 会将该对象的属性覆盖掉当前组件的 *state*
|
||||
- 参数:错误对象
|
||||
- 通常,**<u>该函数用于改变状态</u>**
|
||||
|
||||
- *componentDidCatch* 实例方法
|
||||
- 运行时间点:渲染子组件的过程中,发生错误,更新页面之后(整个应用已经崩溃了,之后再重新渲染整个应用,当然会排除有问题的那一部分UI,那一部分渲染降级UI),由于其运行时间点比较靠后,**<u>因此不太会在该函数中改变状态</u>**
|
||||
- 通常,**<u>该函数用于记录错误消息</u>**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>最佳实践,使用 *static getDerivedStateFromError* 渲染备用 *UI* ,使用 *componentDidCatch* 打印错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
之后,我们就使用这个错误边界组件来包裹要忽略渲染错误的子组件,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import ChildCom3 from "./ChildCom3";
|
||||
import ErrorBoundary from "./ErrorBoundary"
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "300px",
|
||||
height: "300px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<ErrorBoundary>
|
||||
<ChildCom3 />
|
||||
</ErrorBoundary>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有了错误边界组件后,*ChildCom3* 组件中的渲染错误并不会导致整个应用崩溃。效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-12-08-065524.png" alt="image-20221208145524497" style="zoom:67%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
最后需要注意的是,错误边界组件主要是用来捕获 *UI* 渲染时的错误,因此如下场景中错误是无法捕获的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 事件处理
|
||||
- 异步代码
|
||||
- 服务端渲染
|
||||
- 它自身抛出来的错误
|
||||
|
||||
总之,错误边界组件仅能过处理**渲染子组件期间**的**同步错误**。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
18
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
<div id="modal"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
18
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/src/App.jsx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1";
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2";
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
padding: "10px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
App组件
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
<ChildCom2 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom3 from "./ChildCom3";
|
||||
import ErrorBoundary from './ErrorBoundary';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '300px',
|
||||
height: '300px',
|
||||
border: '1px solid'
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<ErrorBoundary>
|
||||
<ChildCom3 />
|
||||
</ErrorBoundary>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom2() {
|
||||
// throw new Error('err!!!');
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: '300px',
|
||||
height: '300px',
|
||||
border: '1px solid'
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom2
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom2;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom4 from "./ChildCom4";
|
||||
|
||||
function getData() {
|
||||
return ["苹果", "香蕉", "西瓜"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom3() {
|
||||
|
||||
const arr = getData();
|
||||
|
||||
const lis = arr.map((it, index) => (<li key={index}>{it}</li>))
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid'
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
{lis}
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
<ChildCom4/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom3;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function getData() {
|
||||
// return ["HTML", "CSS", "JS"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function ChildCom3() {
|
||||
|
||||
const arr = getData();
|
||||
|
||||
const lis = arr.map((it, index) => (<li key={index}>{it}</li>))
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<ul
|
||||
style={{
|
||||
border: '1px solid'
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
{lis}
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom3;
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
// 这边需要你维护一个状态,该状态用来标记是否有错误
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
hasError: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
|
||||
console.log("error:::",error);
|
||||
return {
|
||||
hasError: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
|
||||
console.log("error>>>", error);
|
||||
console.log("errorInfo>>>", errorInfo);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
if (this.state.hasError) {
|
||||
// 说明有错误,渲染自定义的降级 UI
|
||||
return (<div>出错了!!</div>);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 没有进入上面的 if,说明没有错误,那直接渲染子组件树
|
||||
return this.props.children;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
8
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/src/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
|
||||
import App from './App';
|
||||
|
||||
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
|
||||
root.render(
|
||||
<App />
|
||||
);
|
||||
80
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-7. 错误边界/课堂代码/my-app/src/utils/tools.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 格式化时间戳
|
||||
* @param {*} timestamp
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export function formatDate(timestamp, part) {
|
||||
if (!timestamp) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let date = new Date(parseInt(timestamp));
|
||||
|
||||
let year = date.getFullYear(); // 年
|
||||
let month = date.getMonth() + 1; // 月
|
||||
let day = date.getDate(); // 日
|
||||
|
||||
let hour = date.getHours(); // 时
|
||||
let minutes = date.getMinutes(); // 分
|
||||
let seconds = date.getSeconds(); // 秒
|
||||
|
||||
let weekArr = [
|
||||
"星期日",
|
||||
"星期一",
|
||||
"星期二",
|
||||
"星期三",
|
||||
"星期四",
|
||||
"星期五",
|
||||
"星期六",
|
||||
];
|
||||
let week = weekArr[date.getDay()];
|
||||
|
||||
// 需要给一位数前面加 0
|
||||
// 9 点 ----> 09:45:03
|
||||
|
||||
if (month >= 1 && month <= 9) {
|
||||
// month += '0'; // a += b ----> a = a + b
|
||||
month = "0" + month;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (day >= 0 && day <= 9) {
|
||||
day = "0" + day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (hour >= 0 && hour <= 9) {
|
||||
hour = "0" + hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minutes >= 0 && minutes <= 9) {
|
||||
minutes = "0" + minutes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (seconds >= 0 && seconds <= 9) {
|
||||
seconds = "0" + seconds;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var str = "";
|
||||
|
||||
switch (part) {
|
||||
case "year": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} `;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "year-time": {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "time-week": {
|
||||
str = `${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
str = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minutes}:${seconds} ${week}`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
700
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课件资料/8. 组件渲染性能优化.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,700 @@
|
||||
# 8. 组件渲染性能优化
|
||||
|
||||
在本小节,我们将会探讨组件在渲染时,如何优化渲染性能问题。
|
||||
|
||||
涉及到的内容会包含 *shouldComponentUpdate、PureComnent、React.memo、useMemo、useCallback* 等。
|
||||
|
||||
## *shouldComponentUpdate* 与 *PureComnent*
|
||||
|
||||
*shouldComponentUpdate* 与 *PureComnent* 都与类组件相关,所以下面会以类组件来示例。
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
counter: 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h1>App 组件</h1>
|
||||
<div>{this.state.counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => this.setState({
|
||||
counter : 1
|
||||
})}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们书写了一个简单的计数器,按钮在点击的时候仍然是设置 *counter* 的值为 *1*,不过,虽然 *counter* 的值没有变,整个组件仍然是重新渲染了的。显然,这一次渲染是没有必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
此时,我们就可以使用 *shouldComponentUpdate* 来进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
文档地址:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html#shouldcomponentupdate*
|
||||
|
||||
当 *props* 或 *state* 发生变化时,*shouldComponentUpdate* 会在渲染执行之前被调用。返回值默认为 *true*。首次渲染或使用 *forceUpdate* 方法时不会调用该方法。
|
||||
|
||||
下面我们来使用 *shouldComponentUpdate* 优化上面的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { Component } from 'react'
|
||||
import { objectEqual } from "./utils/tools"
|
||||
|
||||
export default class App extends Component {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
counter: 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param {*} nextProps 新的 props
|
||||
* @param {*} nextState 新的 state
|
||||
* @returns
|
||||
*/
|
||||
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
|
||||
// shouldComponentUpdate会根据返回值来决定是否重新渲染
|
||||
// 默认是 true,要重新渲染
|
||||
// 如果返回 false,则不会重新渲染
|
||||
// 我们就需要将当前的 props 和 state 与新的 props 和 state 进行一个比较
|
||||
if (objectEqual(this.props, nextProps) && objectEqual(this.state, nextState)) {
|
||||
// 如果新旧 props 和 state 都是相同的,那么就返回 false,不需要重新渲染
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h1>App 组件</h1>
|
||||
<div>{this.state.counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => this.setState({
|
||||
counter: Math.floor(Math.random() * 3 + 1)
|
||||
})}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们在类组件中书写了一个 *shouldComponentUpdate* 的生命周期钩子函数,该函数会在渲染执行之前被调用,函数内部能够接收到新的属性和新的状态,我们要做的就是让新的属性和状态和当前的属性以及状态进行浅比较,如果相同则返回 *false*,也就是不重新渲染。
|
||||
|
||||
此方法仅作为性能优化的方式而存在,不要企图依靠此方法来“阻止”渲染。另外,现在 *React* 官方已经提供了 *PureComponent*,因此一般情况下我们是不需要手写 *shouldComponentUpdate* 的。
|
||||
|
||||
*PureComponent* 文档:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#reactpurecomponent*
|
||||
|
||||
>**<u>*React.PureComponent* 与 *React.Component* 很相似。两者的区别在于 *React.Component* 并未实现 *shouldComponentUpdate( )*,而 *React.PureComponent* 中以浅层对比 *prop* 和 *state* 的方式来实现了该函数。</u>**
|
||||
|
||||
例如我们将上面的示例直接修改为 *PureComponent*,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
|
||||
export default class App extends PureComponent {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
counter: 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h1>App 组件</h1>
|
||||
<div>{this.state.counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => this.setState({
|
||||
counter: Math.floor(Math.random() * 3 + 1)
|
||||
})}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,效果相同,但是代码精简了很多。在使用 *PureComponent* 的时候,有一点一定要注意,这也是官方所强调,就是内部做的是浅比较,这意味下面的代码是无法更新的:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
|
||||
export default class App extends PureComponent {
|
||||
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
super();
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
stu: ["张三", "李四"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addStuHandle = () => {
|
||||
this.state.stu.push("王武");
|
||||
this.setState({
|
||||
stu: this.state.stu
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
const stuLis = this.state.stu.map((it, index) => (<li key={index}>{it}</li>))
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h1>App 组件</h1>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
{stuLis}
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
<button onClick={this.addStuHandle}>添加学生</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
究其原因,是因为数组的地址并没有发生更改,而是数组内部发生的更改,但是 **<u>*PureComponent* 是浅比较,会认为数组并没有发生更改,因此不会进行渲染更新。</u>**(如果使用 *Component* 则是没有问题的,因为 *React.Component* 并未实现 *shouldComponentUpdate*)
|
||||
|
||||
但是不管怎样,我们都应该返回一个新的数组,而不是把原来的数组赋值给 *stu*:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
addStuHandle = () => {
|
||||
const arr = [...this.state.stu]
|
||||
arr.push("王武");
|
||||
this.setState({
|
||||
stu: arr
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## *React.memo*
|
||||
|
||||
*shouldComponentUpdate* 与 *PureComnent* 主要是优化类组件的渲染性能,那么如果是函数组件该怎么办呢?
|
||||
|
||||
在 *React* 中,为我们提供了 *React.memo*。
|
||||
|
||||
文档地址:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#reactmemo*
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个高阶组件,如果你的组件在相同 *props* 的情况下渲染相同的结果,那么你可以通过将其包装在 *React.memo* 中调用,以此通过记忆组件渲染结果的方式来提高组件的性能表现。
|
||||
|
||||
来看一个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [counter1, setCounter1] = useState(1);
|
||||
const [counter2, setCounter2] = useState(1);
|
||||
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div>{counter1}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCounter1(counter1 + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 counter={counter2} setCounter={setCounter2} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react"
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
console.log("ChildCom1 渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div>ChildCom1</div>
|
||||
<div>{props.counter}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的示例中,*App* 根组件中定义了两个状态 *counter1* 和 *counter2*,在 *App* 组件内部修改 *counter1*,然后 *counter2* 作为 *porps* 传递给子组件,此时我们修改 *counter1* 的状态时,子组件也会跟着更新,原因很简单,因为父组件更新了,那你子组件当然要重新更新。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,我们发现,其实**<u>子组件的更新是没有必要的,因为传递给子组件的 *props* 并没有发生变化</u>**,此时我们就可以使用 *React.memo*,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react"
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
console.log("ChildCom1 渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div>ChildCom1</div>
|
||||
<div>{props.counter}</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default React.memo(ChildCom1);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后我们再更新 *counter1* 时,由于传递给子组件的 *counter2* 这个 *props* 属性并没有变化,因此子组件不会更新。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:默认情况下其只会对复杂对象做浅层对比,如果你想要控制对比过程,那么请将自定义的比较函数通过第二个参数传入来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [counter1, setCounter1] = useState(2);
|
||||
const [stu, setStu] = useState(["张三","李四"]);
|
||||
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
|
||||
function clickHandle(){
|
||||
setCounter1(counter1 + 1);
|
||||
stu.push("王武");
|
||||
setStu(stu)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div>{counter1}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={clickHandle}>+1</button>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 stu={stu} setStu={setStu} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react"
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
console.log("ChildCom1 渲染了")
|
||||
const lis = props.stu.map((it,index)=>(<li key={index}>{it}</li>))
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div>ChildCom1</div>
|
||||
<ul>{lis}</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default React.memo(ChildCom1);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个例子和我们之前的 *PureComponent* 所举的例子很相似,由于是在原来的数组上面进行的修改,数组的地址并没有发生变化,因此 *React.memo* 返回的组件并不会更新。
|
||||
|
||||
>实际上 *React.memo* 的源码就是返回一个 *PureComponent* 组件:
|
||||
>```js
|
||||
>function memo(FuncComp){
|
||||
> return class Memo extends PureComponent{
|
||||
> render(){
|
||||
> return <>{FuncComp(this.props)}</>
|
||||
> }
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>}
|
||||
>```
|
||||
|
||||
此时要解决这个问题也很简单,和前面一样,直接返回一个新的数组,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function clickHandle(){
|
||||
setCounter1(counter1 + 1);
|
||||
const arr = [...stu];
|
||||
arr.push("王武");
|
||||
setStu(arr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
另外,在使用 *React.memo* 的时候还支持传入第二个自定义的比较函数参数,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function MyComponent(props) {
|
||||
/* 使用 props 渲染 */
|
||||
}
|
||||
function areEqual(prevProps, nextProps) {
|
||||
/*
|
||||
如果把 nextProps 传入 render 方法的返回结果与
|
||||
将 prevProps 传入 render 方法的返回结果一致则返回 true,
|
||||
否则返回 false
|
||||
*/
|
||||
}
|
||||
export default React.memo(MyComponent, areEqual);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## *useCallback*
|
||||
|
||||
正常情况下,如果组件各自内部维护自己的数据,那么组件更新的时候相互并不会影响,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
*App* 根组件对应样式:
|
||||
|
||||
```css
|
||||
.container {
|
||||
width: 500px;
|
||||
height: 200px;
|
||||
border: 1px solid;
|
||||
margin: 0 auto;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btnContainer {
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.childComContainer {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
justify-content: space-between;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*App* 根组件,引入了 *ChildCom1* 和 *ChildCom2* 这两个子组件:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
|
||||
import styles from "./css/App.module.css"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
|
||||
console.log("App渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.container}>
|
||||
<div className={styles.btnContainer}>
|
||||
<div>{counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCounter(counter + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div className={styles.childComContainer}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 />
|
||||
<ChildCom2 />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*ChildCom1* 子组件:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState } from "react"
|
||||
function ChildCom1() {
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
|
||||
console.log("ChildCom1 渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
height: "100px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<div>{counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCounter(counter + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>*ChildCom2* 组件基本相同
|
||||
|
||||
此时在我们的应用中,**<u>各个组件内部维护了自身的数据,组件内部数据的更新并不会影响到同级组件和祖级组件</u>**。效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-12-08-065641.gif" alt="iShot_2022-12-02_15.46.37" style="zoom:67%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,父组件的更新会导致两个子组件更新,这是正常的,子组件各自的更新不会影响其他组件。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,倘若两个子组件的数据都来自于父组件,情况就不一样了。
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们把上面的代码稍作修改,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
*App.jsx* 根组件,为两个子组件提供了数据以及修改数据的方法
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
|
||||
import styles from "./css/App.module.css"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
|
||||
const [counter1, setCounter1] = useState(0);
|
||||
const [counter2, setCounter2] = useState(0);
|
||||
console.log("App渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.container}>
|
||||
<div className={styles.btnContainer}>
|
||||
<div>{counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCounter(counter + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div className={styles.childComContainer}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 counter={counter1} setCounter={setCounter1}/>
|
||||
<ChildCom2 counter={counter2} setCounter={setCounter2}/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*ChildCom1* 子组件接收从父组件传递过来的数据,并调用父组件传递过来的方法修改数据
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
console.log("ChildCom1 渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
height: "100px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<div>{props.counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => props.setCounter(props.counter + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default ChildCom1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2022-12-08-065708.gif" alt="iShot_2022-12-02_15.52.31" style="zoom:67%;" />
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,在更新子组件的数据时,由于数据是从父组件传递下去的,相当于更新了父组件数据,那么父组件就会重新渲染,最终导致的结果就是父组件下面所有的子组件都重新渲染了。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们会想到使用前面所讲的 *React.memo* 来解决这个问题,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React from "react"
|
||||
function ChildCom1(props) {
|
||||
console.log("ChildCom1 渲染了")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div style={{
|
||||
width: "200px",
|
||||
height: "100px",
|
||||
border: "1px solid"
|
||||
}}>
|
||||
ChildCom1
|
||||
<div>{props.counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => props.setCounter(props.counter + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 相同的 props 传入的时候该组件不需要重新渲染
|
||||
export default React.memo(ChildCom1);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们使用 *React.memo* 来缓存 *ChildCom1* 组件,这样在相同的 *props* 传入时,该组件不会重新渲染。
|
||||
|
||||
但是假设此时 *App* 组件还有一个单独的函数传入,那就不那么好使了:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
// App 组件自身有一个状态
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了")
|
||||
|
||||
function test() {
|
||||
console.log("test");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.container}>
|
||||
{/* ... */}
|
||||
|
||||
<div className={styles.childComContainer}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 counter={counter1} setCounter={setCounter1} test={test} />
|
||||
<ChildCom2 counter={counter2} setCounter={setCounter2} test={test} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们还向两个子组件传入了一个 *test* 函数,由于每次 *App* 组件的重新渲染会生成新的 *test* 函数,所以对于两个子组件来讲传入的 *test* 导致 *props* 不同所以都会重新渲染。
|
||||
|
||||
此时就可以使用 *useCallback* 来解决这个问题,语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const memoizedCallback = useCallback(
|
||||
() => {
|
||||
doSomething(a, b);
|
||||
},
|
||||
[a, b],
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
把内联回调函数及依赖项数组作为参数传入 *useCallback*,它将返回该回调函数的 *memoized* 版本,该回调函数仅在某个依赖项改变时才会更新。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们来使用 *useCallback* 优化上面的问题,对 *App.jsx* 做如下的修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { useState, useCallback } from 'react';
|
||||
import ChildCom1 from "./components/ChildCom1"
|
||||
import ChildCom2 from "./components/ChildCom2"
|
||||
|
||||
import styles from "./css/App.module.css"
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(1); // 这是 App 组件自身维护的状态
|
||||
const [counter1, setCounter1] = useState(1); // 这是要传递给 ChildCom1 组件的数据
|
||||
const [counter2, setCounter2] = useState(1); // 这是要传递给 ChildCom2 组件的数据
|
||||
|
||||
console.log("App组件渲染了")
|
||||
|
||||
// 每次重新渲染的时候,就会生成一个全新的 test 函数
|
||||
// 使用了 useCallback 之后,我们针对 test 函数做了一个缓存
|
||||
const newTest = useCallback(function test(){
|
||||
console.log("test触发了")
|
||||
},[])
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.container}>
|
||||
{/* 自身的计数器 */}
|
||||
<div className={styles.btnContainer}>
|
||||
<div>counter:{counter}</div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCounter(counter + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
{/* 使用子组件 */}
|
||||
<div className={styles.childComContainer}>
|
||||
<ChildCom1 counter={counter1} setCounter={setCounter1} test={newTest}/>
|
||||
<ChildCom2 counter={counter2} setCounter={setCounter2} test={newTest}/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的代码中,我们对 *test* 函数做了缓存,从而保证每次传入到子组件的这个 *props* 和之前是相同的。
|
||||
|
||||
**<u>记住:*useCallback* 主要就是对函数进行缓存</u>**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## *useMemo*
|
||||
|
||||
最后要介绍的是 *useMemo*,其语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const memoizedValue = useMemo(() => computeExpensiveValue(a, b), [a, b]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
主要用于返回一个 *memoized* 值。
|
||||
|
||||
文档地址:*https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/hooks-reference.html#usememo*
|
||||
|
||||
某些时候,组件中某些值需要根据状态进行一个二次计算(类似于 *Vue* 中的计算属性),由于函数组件一旦重新渲染,就会重新执行整个函数,这就导致之前的二次计算也会重新执行一次,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { useState } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [count, setCount] = useState(1);
|
||||
const [val, setValue] = useState('');
|
||||
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
|
||||
function getNum() {
|
||||
console.log('调用了!!!');
|
||||
return count + 100;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h4>总和:{getNum()}</h4>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
{/* 文本框的输入会导致整个组件重新渲染 */}
|
||||
<input value={val} onChange={event => setValue(event.target.value)} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的示例中,文本框的输入会导致整个 *App* 组件重新渲染,但是 *count* 的值是没有改变的,所以 *getNum* 这个函数也是没有必要重新执行的。
|
||||
|
||||
此时,我们就可以使用 *useMemo* 来缓存这个计算值,除非 *count* 变了,否则直接使用缓存值,不需要重新做二次计算(调用 *getNum*)。
|
||||
|
||||
如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import React, { useState,useMemo } from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
function App() {
|
||||
|
||||
const [count, setCount] = useState(1);
|
||||
const [val, setValue] = useState('');
|
||||
|
||||
console.log("App 渲染了");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
const getNum = useMemo(() => {
|
||||
console.log('调用了!!!!!');
|
||||
return count + 100;
|
||||
}, [count])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h4>总和:{getNum}</h4>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+1</button>
|
||||
{/* 文本框的输入会导致整个组件重新渲染 */}
|
||||
<input value={val} onChange={event => setValue(event.target.value)} />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default App;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的示例中,我们使用了 *useMemo* 来缓存二次计算的值,并设置了依赖项 *count*,只有在 *count* 发生改变时,才会重新执行二次计算。
|
||||
|
||||
>面试题:*useMemo* 和 *useCallback* 的区别及使用场景?
|
||||
>
|
||||
>*useMemo* 和 *useCallback* 接收的参数都是一样,第一个参数为回调,第二个参数为要依赖的数据。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>共同作用:
|
||||
>仅仅依赖数据发生变化,才会去更新缓存。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>两者区别:
|
||||
>1. *useMemo* 计算结果是 *return* 回来的值, 主要用于缓存计算结果的值。应用场景如:需要进行二次计算的状态
|
||||
>2. *useCallback* 计算结果是函数, 主要用于缓存函数,应用场景如: 需要缓存的函数,因为函数式组件每次任何一个 *state* 的变化,整个组件都会被重新刷新,一些函数是没有必要被重新刷新的,此时就应该缓存起来,提高性能,和减少资源浪费。
|
||||
|
||||
-*EOF*-
|
||||
23
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课堂代码/my-app/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
|
||||
|
||||
# dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
/.pnp
|
||||
.pnp.js
|
||||
|
||||
# testing
|
||||
/coverage
|
||||
|
||||
# production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
70
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课堂代码/my-app/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Getting Started with Create React App
|
||||
|
||||
This project was bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
In the project directory, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm start`
|
||||
|
||||
Runs the app in the development mode.\
|
||||
Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) to view it in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The page will reload when you make changes.\
|
||||
You may also see any lint errors in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm test`
|
||||
|
||||
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.\
|
||||
See the section about [running tests](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/running-tests) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build`
|
||||
|
||||
Builds the app for production to the `build` folder.\
|
||||
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.\
|
||||
Your app is ready to be deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
See the section about [deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run eject`
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you `eject`, you can't go back!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can `eject` at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except `eject` will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you're on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to ever use `eject`. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn't feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn't be useful if you couldn't customize it when you are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn More
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more in the [Create React App documentation](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/getting-started).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn React, check out the [React documentation](https://reactjs.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Splitting
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting)
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Bundle Size
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Progressive Web App
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app)
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
### Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment)
|
||||
|
||||
### `npm run build` fails to minify
|
||||
|
||||
This section has moved here: [https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify](https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify)
|
||||
28006
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课堂代码/my-app/package-lock.json
generated
Normal file
39
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课堂代码/my-app/package.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-app",
|
||||
"version": "0.1.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.16.5",
|
||||
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
|
||||
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
|
||||
"prop-types": "^15.8.1",
|
||||
"react": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
|
||||
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
|
||||
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"start": "react-scripts start",
|
||||
"build": "react-scripts build",
|
||||
"test": "react-scripts test",
|
||||
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"eslintConfig": {
|
||||
"extends": [
|
||||
"react-app",
|
||||
"react-app/jest"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.2%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课堂代码/my-app/public/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.8 KiB |
18
就业篇/01. 第一章/1-8. 组件渲染性能优化/课堂代码/my-app/public/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
|
||||
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
|
||||
<meta
|
||||
name="description"
|
||||
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<title>React App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="root"></div>
|
||||
<div id="modal"></div>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||