313 lines
6.9 KiB
Markdown
313 lines
6.9 KiB
Markdown
# 面试题考点
|
||
|
||
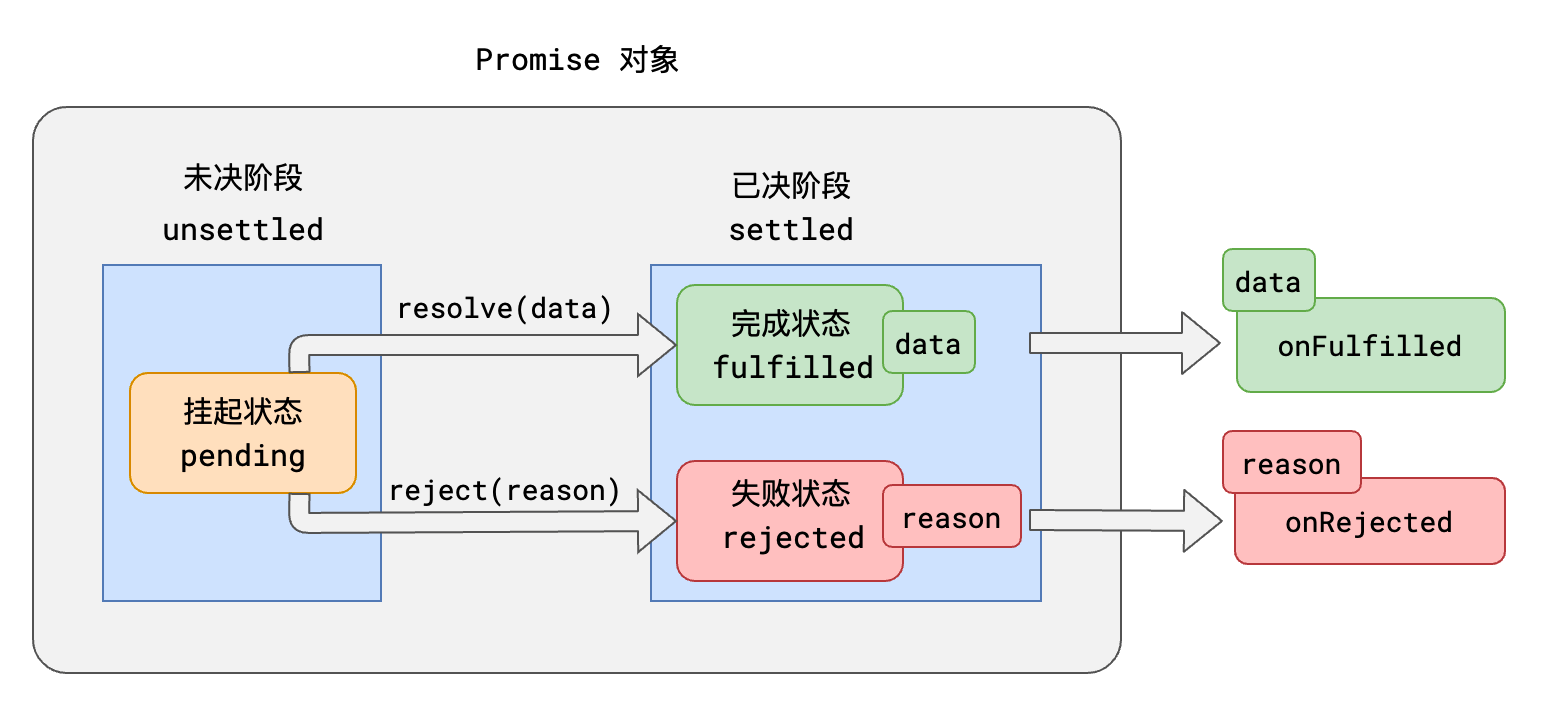
## Promise的基本概念
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
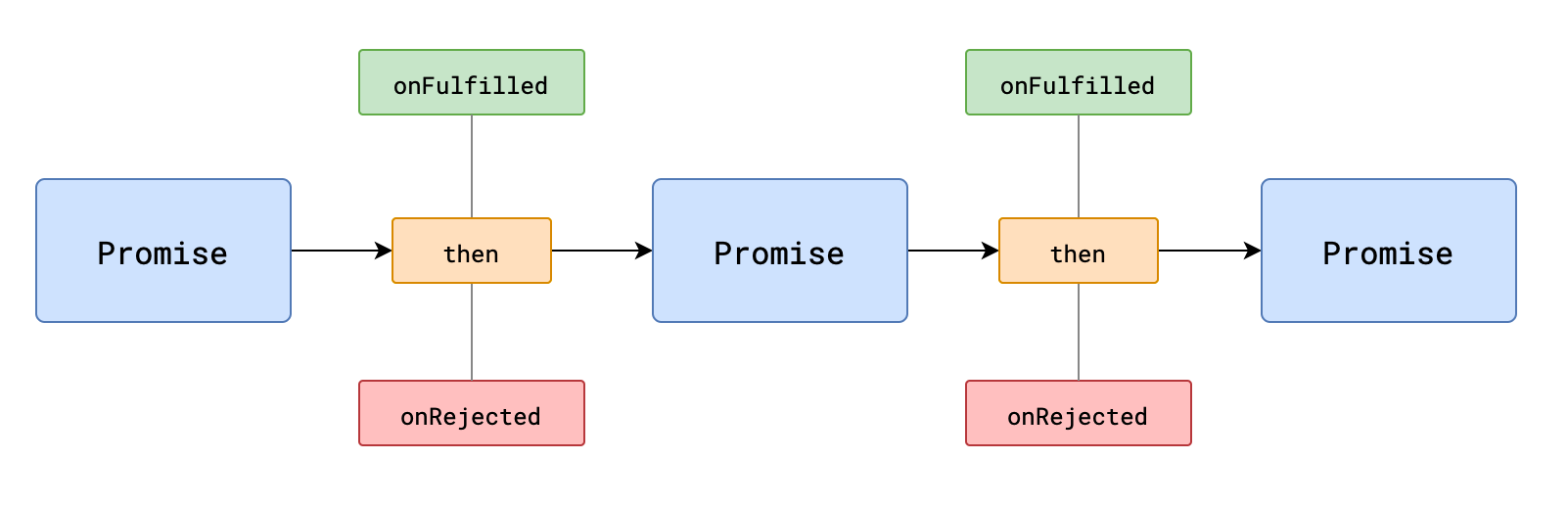
## 链式调用规则
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
1. then方法必定会返回一个新的Promise
|
||
|
||
可理解为`后续处理也是一个任务`
|
||
|
||
2. 新任务的状态取决于后续处理:
|
||
|
||
- 若没有相关的后续处理,新任务的状态和前任务一致,数据为前任务的数据
|
||
|
||
- 若有后续处理但还未执行,新任务挂起。
|
||
- 若后续处理执行了,则根据后续处理的情况确定新任务的状态
|
||
- 后续处理执行无错,新任务的状态为完成,数据为后续处理的返回值
|
||
- 后续处理执行有错,新任务的状态为失败,数据为异常对象
|
||
- 后续执行后返回的是一个任务对象,新任务的状态和数据与该任务对象一致
|
||
|
||
## Promise的静态方法
|
||
|
||
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|
||
| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||
| Promise.resolve(data) | 直接返回一个完成状态的任务 |
|
||
| Promise.reject(reason) | 直接返回一个拒绝状态的任务 |
|
||
| Promise.all(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组全部成功则成功<br />任何一个失败则失败 |
|
||
| Promise.any(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组任一成功则成功<br />任务全部失败则失败 |
|
||
| Promise.allSettled(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组全部已决则成功<br />该任务不会失败 |
|
||
| Promise.race(任务数组) | 返回一个任务<br />任务数组任一已决则已决,状态和其一致 |
|
||
| | |
|
||
|
||
## async和await
|
||
|
||
有了Promise,异步任务就有了一种统一的处理方式
|
||
|
||
有了统一的处理方式,ES官方就可以对其进一步优化
|
||
|
||
ES7推出了两个关键字`async`和`await`,用于更加优雅的表达Promise
|
||
|
||
### async
|
||
|
||
async关键字用于修饰函数,被它修饰的函数,一定返回Promise
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function method1(){
|
||
return 1; // 该函数的返回值是Promise完成后的数据
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
method1(); // Promise { 1 }
|
||
|
||
async function method2(){
|
||
return Promise.resolve(1); // 若返回的是Promise,则method得到的Promise状态和其一致
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
method2(); // Promise { 1 }
|
||
|
||
async function method3(){
|
||
throw new Error(1); // 若执行过程报错,则任务是rejected
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
method3(); // Promise { <rejected> Error(1) }
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### await
|
||
|
||
`await`关键字表示等待某个Promise完成,**它必须用于`async`函数中**
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function method(){
|
||
const n = await Promise.resolve(1);
|
||
console.log(n); // 1
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 上面的函数等同于
|
||
function method(){
|
||
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
|
||
Promise.resolve(1).then(n=>{
|
||
console.log(n);
|
||
resolve(1)
|
||
})
|
||
})
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
`await`也可以等待其他数据
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function method(){
|
||
const n = await 1; // 等同于 await Promise.resolve(1)
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果需要针对失败的任务进行处理,可以使用`try-catch`语法
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function method(){
|
||
try{
|
||
const n = await Promise.reject(123); // 这句代码将抛出异常
|
||
console.log('成功', n)
|
||
}
|
||
catch(err){
|
||
console.log('失败', err)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
method(); // 输出: 失败 123
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 事件循环
|
||
|
||
根据目前所学,进入事件队列的函数有以下几种:
|
||
|
||
- `setTimeout`的回调,宏任务(macro task)
|
||
- `setInterval`的回调,宏任务(macro task)
|
||
- Promise的`then`函数回调,**微任务**(micro task)
|
||
- `requestAnimationFrame`的回调,宏任务(macro task)
|
||
- 事件处理函数,宏任务(macro task)
|
||
|
||
# 面试题
|
||
|
||
1. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||
console.log(1);
|
||
resolve();
|
||
console.log(2);
|
||
})
|
||
|
||
promise.then(() => {
|
||
console.log(3);
|
||
})
|
||
|
||
console.log(4);
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
2. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||
console.log(1);
|
||
setTimeout(()=>{
|
||
console.log(2)
|
||
resolve();
|
||
console.log(3);
|
||
})
|
||
})
|
||
|
||
promise.then(() => {
|
||
console.log(4);
|
||
})
|
||
|
||
console.log(5);
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
3. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||
resolve()
|
||
}, 1000)
|
||
})
|
||
const promise2 = promise1.catch(() => {
|
||
return 2;
|
||
})
|
||
|
||
console.log('promise1', promise1)
|
||
console.log('promise2', promise2)
|
||
|
||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||
console.log('promise1', promise1)
|
||
console.log('promise2', promise2)
|
||
}, 2000)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
4. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function m(){
|
||
const n = await 1;
|
||
console.log(n);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
m();
|
||
console.log(2);
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
5. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function m(){
|
||
const n = await 1;
|
||
console.log(n);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
(async ()=>{
|
||
await m();
|
||
console.log(2);
|
||
})();
|
||
|
||
console.log(3);
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
6. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function m1(){
|
||
return 1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
async function m2(){
|
||
const n = await m1();
|
||
console.log(n)
|
||
return 2;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
async function m3(){
|
||
const n = m2();
|
||
console.log(n);
|
||
return 3;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
m3().then(n=>{
|
||
console.log(n);
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
m3();
|
||
|
||
console.log(4);
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
7. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
Promise.resolve(1)
|
||
.then(2)
|
||
.then(Promise.resolve(3))
|
||
.then(console.log)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
8. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
var a;
|
||
var b = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||
console.log('promise1');
|
||
setTimeout(()=>{
|
||
resolve();
|
||
}, 1000);
|
||
}).then(() => {
|
||
console.log('promise2');
|
||
}).then(() => {
|
||
console.log('promise3');
|
||
}).then(() => {
|
||
console.log('promise4');
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
a = new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
|
||
console.log(a);
|
||
await b;
|
||
console.log(a);
|
||
console.log('after1');
|
||
await a
|
||
resolve(true);
|
||
console.log('after2');
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
console.log('end');
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
9. 下面代码的输出结果是什么
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
async function async1() {
|
||
console.log('async1 start');
|
||
await async2();
|
||
console.log('async1 end');
|
||
}
|
||
async function async2() {
|
||
console.log('async2');
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
console.log('script start');
|
||
|
||
setTimeout(function() {
|
||
console.log('setTimeout');
|
||
}, 0)
|
||
|
||
async1();
|
||
|
||
new Promise(function(resolve) {
|
||
console.log('promise1');
|
||
resolve();
|
||
}).then(function() {
|
||
console.log('promise2');
|
||
});
|
||
console.log('script end');
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|