152 lines
4.9 KiB
Markdown
152 lines
4.9 KiB
Markdown
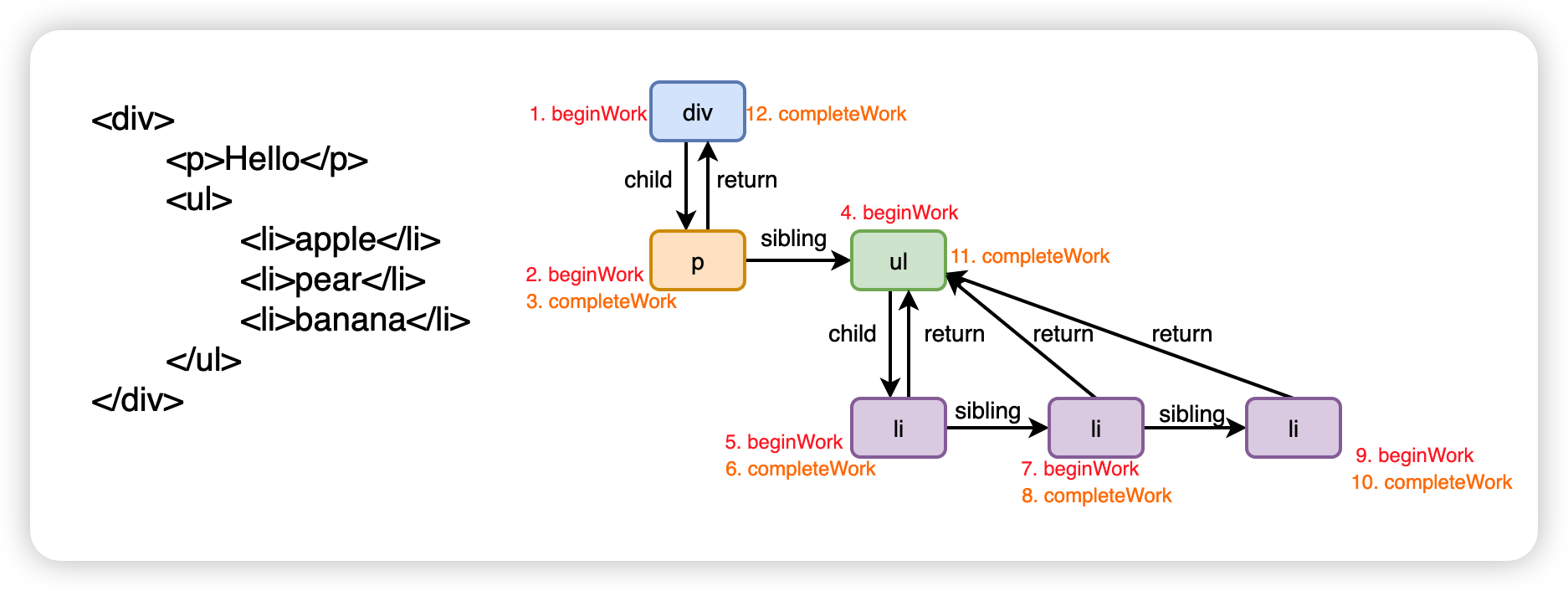
# beginWork工作流程
|
||
|
||
> 面试题:beginWork 中主要做一些什么工作?整体的流程是怎样的?
|
||
|
||
Reconciler(协调器) 是 Render 阶段的第二阶段工作,整个工作的过程可以分为“递”和“归”:
|
||
|
||
- 递:beginWork
|
||
- 归:completeWork
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
beginWork 方法主要是根据传入的 FiberNode 创建下一级的 FiberNode。
|
||
|
||
整个 beginWork 方法的流程如下图所示:
|
||
|
||
<img src="https://xiejie-typora.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/2023-03-01-015305.png" alt="image-20230301095305141" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
||
|
||
首先在 beginWork 中,会判断当前的流程是 mount(初次渲染)还是update(更新),判断的依据就是 currentFiberNode 是否存在
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
if(current !== null){
|
||
// 说明 CurrentFiberNode 存在,应该是 update
|
||
} else {
|
||
// 应该是 mount
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果是 update,接下来会判断 wipFiberNode 是否能够复用,如果不能够复用,那么 update 和 mount 的流程大体上一致:
|
||
|
||
- 根据 wip.tag 进行不同的分支处理
|
||
- 根据 reconcile 算法生成下一级的 FiberNode(diff 算法)
|
||
|
||
无法复用的 update 流程和 mount 流程大体一致,主要区别在于是否会生成带副作用标记 flags 的 FiberNode
|
||
|
||
beginWork 方法的代码结构如下:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
// current 代表的是 currentFiberNode
|
||
// workInProgress 代表的是 workInProgressFiberNode,后面我会简称为 wip FiberNode
|
||
function beginWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes) {
|
||
// ...
|
||
if(current !== null) {
|
||
// 进入此分支,说明是更新
|
||
} else {
|
||
// 说明是首次渲染
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// ...
|
||
|
||
// 根据不同的 tag,进入不同的处理逻辑
|
||
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
|
||
case IndeterminateComponent: {
|
||
// ...
|
||
}
|
||
case FunctionComponent : {
|
||
// ...
|
||
}
|
||
case ClassComponent : {
|
||
// ...
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
关于 tag,在 React 源码中定义了 28 种 tag:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
export const FunctionComponent = 0;
|
||
export const ClassComponent = 1;
|
||
export const IndeterminateComponent = 2; // Before we know whether it is function or class
|
||
export const HostRoot = 3; // Root of a host tree. Could be nested inside another node.
|
||
export const HostPortal = 4; // A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer.
|
||
export const HostComponent = 5;
|
||
export const HostText = 6;
|
||
export const Fragment = 7;
|
||
// ...
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
不同的 FiberNode,会有不同的 tag
|
||
|
||
- HostComponent 代表的就是原生组件(div、span、p)
|
||
- FC 在 mount 的时候,对应的 tag 为 IndeterminateComponent,在 update 的时候就会进入 FunctionComponent
|
||
- HostText 表示的是文本元素
|
||
|
||
根据不同的 tag 处理完 FiberNode 之后,根据是mount 还是 update 会进入不同的方法:
|
||
|
||
- mount:mountChildFibers
|
||
- update:reconcileChildFibers
|
||
|
||
这两个方法实际上都是一个叫 ChildReconciler 方法的返回值:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
var reconcileChildFibers = ChildReconciler(true);
|
||
var mountChildFibers = ChildReconciler(false);
|
||
|
||
function ChildReconciler(shouldTrackSideEffects) {}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
也就是说,在 ChildReconciler 方法内容,shouldTrackSideEffects 是一个布尔值
|
||
|
||
- false:不追踪副作用,不做 flags 标记,因为你是 mount 阶段
|
||
- true:要追踪副作用,做 flags 标记,因为是 update 阶段
|
||
|
||
在 ChildReconciler 方法内部,就会根据 shouldTrackSideEffects 做一些不同的处理:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
function placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIndex){
|
||
newFiber.index = newIndex;
|
||
|
||
if(!shouldTrackSideEffects){
|
||
// 说明是初始化
|
||
// 说明不需要标记 Placement
|
||
newFiber.flags |= Forked;
|
||
return lastPlacedIndex
|
||
}
|
||
// ...
|
||
// 说明是更新
|
||
// 标记为 Placement
|
||
newFiber.flags |= Placement;
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
可以看到,在 beginWork 方法内部,也会做一些 flags 标记(主要是在 update 阶段),这些 flags 标记主要和元素的位置有关系:
|
||
|
||
- 标记 ChildDeletion,这个是代表删除操作
|
||
- 标记 Placement,这是代表插入或者移动操作
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 真题解答
|
||
|
||
> 题目:beginWork 中主要做一些什么工作?整体的流程是怎样的?
|
||
>
|
||
> 参考答案:
|
||
>
|
||
> 在 beginWork 会根据是 mount 还是 update 有着不一样的流程。
|
||
>
|
||
> 如果当前的流程是 update,则 WorkInProgressFiberNode 存在对应的 CurrentFiberNode,接下来就判断是否能够复用。
|
||
>
|
||
> 如果无法复用 CurrentFiberNode,那么 mount 和 update 的流程大体上是一致的:
|
||
>
|
||
> - 根据 wip.tag 进入“不同类型元素的处理分支”
|
||
> - 使用 reconcile 算法生成下一级 FiberNode(diff 算法)
|
||
>
|
||
> 两个流程的区别在于“最终是否会为生成的子 FiberNode 标记副作用 flags”
|
||
>
|
||
> 在 beginWork 中,如果标记了副作用的 flags,那么主要与元素的位置相关,包括:
|
||
>
|
||
> - 标记 ChildDeletion,代表删除操作
|
||
> - 标记 Placement,代表插入或移动操作
|